Dogecoin and Pepe maintain to expose robust momentum as meme-coin sentiment heats up beforehand of 2026, with both properties leaning on powerful groups and viral traction to fuel clean rallies. Their upside ability stays substantial, but analysts note that their growth nonetheless depends closely on social media traits and market hype rather than long-term technological price
Ozak AI, by contrast, is drawing far stronger long-term forecasts thanks to its early-stage position, rapidly expanding AI ecosystem, and utility-driven architecture powered by high-speed prediction agents, real-time blockchain analytics, and advanced AI partnerships. With presale demand accelerating and its tech stack positioned for real-world adoption, Ozak AI’s 2026 outlook appears far more promising than sentiment-driven meme coins, giving it the kind of structural advantage that supports exponential, sustainable growth.
DOGE & Pepe Forecast
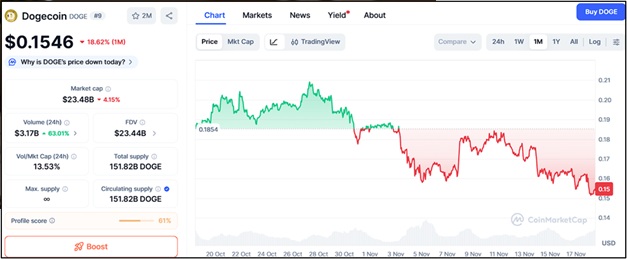
Dogecoin and Pepe continue to capture attention as meme-coin enthusiasm rises once again, with both assets showing renewed strength heading into 2026. Dogecoin currently trades near $0.1546, supported by strong community sentiment and recurring social media momentum. DOGE maintains a bullish structure as long as the price holds above support at $0.148, $0.136, and $0.122, areas where long-term holders typically accumulate. Momentum will depend on whether DOGE can break resistance at $0.167, $0.182, and $0.205, levels that historically trigger large spikes when breached.
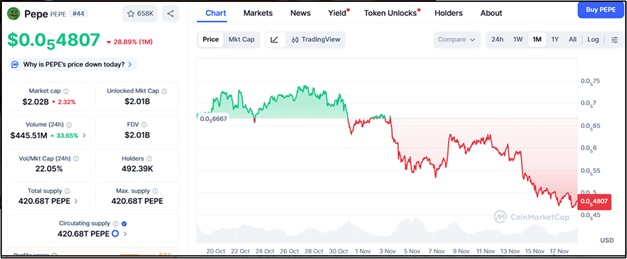
Pepe (PEPE), trading around $0.000004807, also shows considerable strength as one of the fastest-moving small-cap meme coins. PEPE’s trend remains intact as long as the price stays above $0.00000432, $0.00000396, and $0.00000357, while resistance at $0.00000519, $0.00000574, and $0.00000630 defines the next wave of potential upside.
Ozak AI’s Utility and Technology Give It a Much Steeper Growth Curve
Ozak AI (OZ) stands apart from meme-driven assets because its core value comes from real utility, not social speculation. The project integrates AI prediction agents, cross-chain analytics, and intelligent automation built to interpret blockchain data at high speed.
This technology is strengthened through partnerships with Perceptron Network’s 700,000+ nodes, HIVE’s 30-millisecond market signal engine, and SINT’s AI-agent infrastructure—all of which create a functional intelligence layer capable of powering next-generation trading insights, research analytics, and decentralized AI-driven applications. These features give Ozak AI a foundation for sustained demand and adoption, something meme coins fundamentally lack. Because Ozak AI is still in OZ presale stages with a low market valuation, its upside potential for 2026 is significantly larger than DOGE or PEPE.
Ozak AI Presale Momentum Signals a Much Larger 2026 Breakout
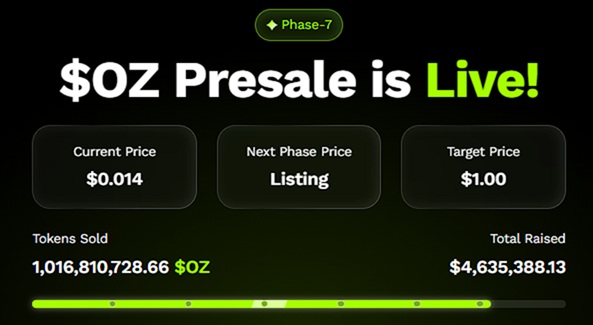
Ozak AI’s presale has already surpassed 1 billion tokens sold and raised over $4.5 million—clear signs of strong early demand. This early participation matters because tokens with meaningful utility, strong partnerships, and low initial valuations often deliver the largest returns during bull cycles.
With no resistance levels limiting early growth and a rapidly expanding narrative around AI-powered crypto tools, Ozak AI sits in prime position for exponential price discovery once listings begin. Analysts believe its 2026 outlook could exceed 50x–100x if the AI narrative continues dominating the tech sector, especially as traditional industries increasingly integrate machine learning, automation, and predictive intelligence.
DOGE and PEPE Look Strong
Dogecoin and Pepe remain strong contenders for impressive returns in the next market cycle, supported by enthusiastic communities and high-volatility upside. Yet their long-term growth still depends heavily on sentiment cycles rather than technological advancement. Ozak AI, by contrast, delivers utility, innovation, and powerful AI-integrated systems—creating a steeper and more sustainable growth trajectory as crypto moves into a more utility-driven era. For traders eyeing 2026 opportunities, DOGE and PEPE offer strong speculative upside, but Ozak AI offers transformational potential—making it one of the most compelling projects to watch in the years ahead.
About Ozak AI
Ozak AI is a blockchain-based crypto project that provides a technology platform that specializes in predictive AI and advanced data analytics for financial markets. Through machine learning algorithms and decentralized network technologies, Ozak AI enables real-time, accurate, and actionable insights to help crypto enthusiasts and businesses make the correct decisions.
For more, visit:
Website: https://ozak.ai/
Telegram: https://t.me/OzakAGI
Twitter: https://x.com/ozakagi








