As an investor, one way of gaining entry into the Nigerian telecomms sector is by the means of MVNO or Mobile Virtual Network Operator licensing which is a comparatively less expensive way of rendering a bouquet of services in the telecomms value chain while achieving ICT inclusion/penetration which remains an important development objective for Nigeria which still has a lot of rural areas that are deficient of any widespread form of modern communication facilities.
This article will be looking at how to secure MVNO licensing and some of the permissible business possibilities that come with acquiring MVNO licensing as well as the compliance framework governing MVNO businesses in Nigeria.
Which government agency is in charge of licensing MVNOs in Nigeria?
MVNO licensing and post-licensing regulatory compliance is under the jurisdiction of the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) pursuant to the Nigerian Communications Act.
What exactly are the objectives of MVNO licensing introduction as envisaged by the NCC?
By introducing MVNO licensing, the NCC aims to achieve the following objectives :-
– Ensuring that all core stakeholders are adequately catered for and protected within a virtual network operator-enabled environment.
– Giving providers of virtual mobile communications services an opportunity to participate in the Telecommunications provisioning market of Nigeria, with an emphasis on improving the Telecomms output of the country.
– The provision of operational guidelines within which Telecomms businesses at the medium scale can flourish within the Nigerian Telecomms sector.
– To provide an avenue for further contribution to the availability and expansion of quality mobile coverage through redundant capacity utilization, active infrastructure sharing, national roaming & other telecommunications elements that enable it.
What exactly is the application scope of the NCC regulatory guidelines governing MVNO businesses in Nigeria?
The scope of NCC regulations governing MVNOs revolve around the following services :-
– Sales & Distribution – providing adequate SIM card sales and distribution channels, registration of subscribers, sales and distribution of devices, etc.
– Tariff & Billing – which involves the development of an efficient tariff structure, ensuring adequate & accurate billing systems, etc.
– Customer Relationship Management – in terms of the provision of necessary customer relationship management systems for catering to customers and their needs, resolving issues and disputes with customers, etc.
– Devices, Application Services & SIM Management – which involves the provision of application of value added services(VAS) , ensuring proper SIM Management operations, meeting Quality of Service(QoS) Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) with regards to VAS and related services,etc.
– International Data & Voice Services.
– Facility Management – which involves ensuring that devices and facilities meet the technical standards outlined by the NCC.
– Core Network Functions & Spectrum Access – which involves the provision of network access to ensure quality delivery of mobile telecommunications services to the end users, ensuring that frequency standards are met for spectrum access,etc.
What exactly is an MVNO?
An MVNO as defined under Nigerian Telecomms regulations is defined as a Telecomms product and service operator that rides on the capacity of a fully licensed Telecomms service provider or Mobile Network Operator (MNO) through the means of a negotiated Wholesale agreement or a revenue sharing agreement for the purpose of bulk purchasing resources from the MNO or Telecomms company for onward delivery to consumers.
What is the actual difference between an MVNO and MNO?
An MVNO simply has no ownership of spectrum elements regardless of its operations model.
Do operational tier systems exist for MVNOs as with other Telecoms business licenses in Nigeria? If they do, which services are allowed to be rendered within those tiers?
Yes, tier-based operational levels exist for MVNO licensing in Nigeria. These tiers and their permissible activities are as follows :-
– Tier 1 (Services Virtual Operator)
1).Within this category, an MVNO can leverage on its ability to offer services to customers without owning any switching or IN(Intelligent Network) infrastructure .
2). MVNOs in this category also do not control any numbering resources & it is the responsibility of the host MNO to provide wholesale capacity to the MVNO for delivery of its products and services.
3). MVNOs in this category can operate in at least one of several operation areas that include brand ownership, sales and distribution channelling, or running SMSC for SMS services.
– Tier 2 ( Simple Facilities Virtual Operator)
1). An MVNO in this category has more control of the Telecomms service value chain that can enable it clearly differentiate itself from its host MNO.
2). While an MVNO on this level cannot possess or acquire core switching & interconnect capabilities but can set up its own IN(Intelligence Network) to provide IN services to customers.
3). MVNOs in this category can establish their own subscriber registers or authentication centers, equipment identity register & home location registers.
4). MVNOs in this category can also own & issue their SIM cards as well as own and operate EIR/HLR/AUC/HSS.
– Tier 3( Core Facilities Virtual Operator)
1). An MVNO in this category can rely on its technical and commercial capacities to launch and operate a full core network with switching & interconnect capabilities.
2). MVNOs in this category rely on their host MNOs to provide radio access capacity at wholesale to deliver its products and services to its customers.
3). MVNOs within this category are typically urged by the NCC to target underserved and unserved areas via subsidized requirements to operate in such areas.
4). MVNOs in this category can own and manage core network elements of switching & interconnection services that include IP Multimedia subsystems, MSC & GMSC, PGSN/PGW, SGSN/SGW & MME.
– Tier 4 ( Virtual Aggregator/Enabler)
1). MVNOs within this category are responsible for aggregating and/or enabling MVNO services within the market and relies on a model in which it stands as a middleman between an MNO and several MVNOs.
2). MVNOs within this capacity can :-
a). install capacity to serve its aggregation/enabling platform; and
b). perform the additional role of a Tier 3 MVNO where the region being served is underserved or unserved.
– Tier 5 ( Unified Virtual Operator)
1). An MVNO in this category can operate on what in reality is a unified license, choosing the services it can offer to customers from Tier 1 to Tier 4.
2). MVNOs in this category can engage in what are known as “shared rural coverage agreements” to enable operations in underserved and unserved regions of Nigeria.
Who are the recognized market players within the MVNO service value chain as outlined by the NCC?
An MVNO service value chain or arrangement is made of the following players :-
– Host Network Operators – which can be :
a). Spectrum license holders
b). Universal access services license holders
c). Digital Mobile license holders
d). VSAT license holders
e). GMPCS license holders
– National Carriers, NLDOs(National Long Distance Operators)& International Gateway Providers :-
Which can provide MVNOs with the capacity to deliver services beyond what the typical host network operator might be able to offer.
It should be noted that MVNOs that enter into agreements with license holders in this sector must be looking to deliver focused services that involve nationwide provisioning and/or international telecomms products and services.
– Infrastructure Companies :-Full facility based MVNOs according to NCC regulations require backhaul connectivity to and from its MSC & the host network operator’s radio access sites. This can be done through agreement-based deployment and maintenance of infrastructure with companies licensed for that purpose.
– Value Added Service (VAS) Aggregators :- The NCC stipulates that VAS provisioning by an operator must be deployed through a VAS Aggregator. MVNOs can also be network providers for VAS Aggregators.
Can Host Network Operators own or purchase equity or share options in MVNOs?
They can only own not more than 10% equity of a Tier 1 – Tier 4 MVNO and 5% of a Tier 5 MVNO.
What are the general obligations/requirements for MVNO licensing in Nigeria?
An applicant for a MVNO license must have the following :-
– A company registered with the Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC).
– A wholesale license leveraging agreement with a host network operator or national carrier.
– Proof of financial capabilities to cover its CAPEX( Capital Expenditure) & OPEX (Operations Expenditure) for strategic business operations.
– Proof of meeting technical requirements set by the NCC.
– Proof of secured reservation or assignment of resources required to operate, numbering resources in particular.
– Proof of local content in ownership and service delivery.
What are the specific requirements for MVNO licensing applicants?
You need to consult your lawyer on this as specific licensing requirements which differ for each NCC Business License.
What are some of the steps involved in an MVNO licensing application process?
The process for MVNO licensing is covered by general NCC processes for Telecomms business individual licenses, however for MVNOs the following steps must be complied with :-
– The completion of an individual introduction form furnishing the NCC with information needed to process a license upon the completion of agreement execution with a host MNO.
– The submission of a Performance Bank Guarantee (PBG), a Financial Bank Guarantee (FBG) & a capital structure summary proving capacity to fund & maintain operations throughout the tenure of the license.
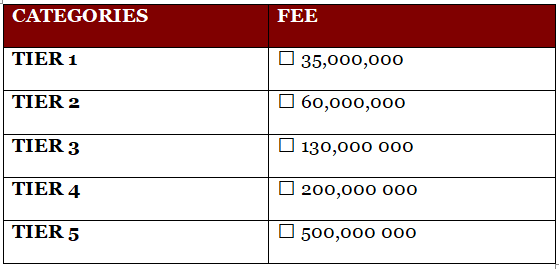
What are the applicable fees for MVNO licensing in Nigeria?
The regulatory fees for MVNO licensing are as follows :-
Tier 1 – 35 Million Naira
Tier 2 – 60 Million Naira
Tier 3 – 130 Million Naira
Tier 4 – 200 Million Naira
Tier 5 – 500 Million Naira
What is the tenure validity period of an MVNO license?
MVNO licenses have a validity tenure of 10(Ten) years.
Can MVNO licenses be renewed, suspended or revoked?
MVNO licenses can be renewed on request by a licensee not later than 12 months before the expiration of a current license. It should be noted that renewal requests can be rejected by the NCC based on a negative performance rating of the applicant’s existing MVNO license tenure.
And yes, an MVNO license revocation or suspension is possible through:-
– An MVNO violating relevant NCC regulations.
– An MVNO violating its agreement with an MNO.
– An MVNO operating beyond the scope of its granted Tier license category.
What are some of the post-licensing compliance requirements for MVNOs as outlined by the NCC?
-The Licensee shall ensure that it complies with the Consumer Code of practice approved by the NCC.
-The Licensee shall be bound by all information provided and its commitments made when acquiring its license, agreeing with a Host MNO and other agreements required to obtain legibility to deliver mobile telecommunications services within the MVNO regulatory regime.
-The Licensee must comply with National Security Protocols and Consumer information protection as required by the regulations of the NCC, where applicable.
-An MVNO Licensee must ensure that it meets the KPIs that pertain to its operating model as detailed within the NCC QoS regulations and guidelines.
Like this:
Like Loading...







