The move by YouTube to allow U.S. creators to be paid using PayPal in PYUSD, the PayPal stablecoin, demonstrates the trend of big platforms to bring blockchain rails on board with no crypto exposure. Owners can store PYUSD in digital wallets or use it with merchants, enjoying the dollar peg, but avoiding the volatility issue. As PYUSD has a market cap of $4 billion, the move underscores the increasing belief in regulated stablecoins.
The reason this development is important is that payments infrastructure is becoming mature and regulatory conditions are becoming more transparent. The use of Big Tech supports the argument of blockchain efficiency in real-life monetizing, anticipating quicker, less expensive settlement in the digital systems. The outcome is a re-emphasis on chains and protocols that are able to support scale without friction.
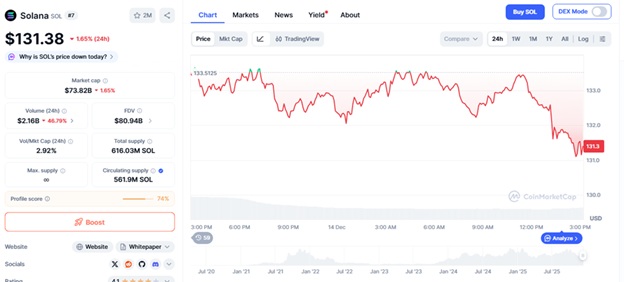
By December 2025, the ecosystem of Solana had hit a market cap of 74.46 billion, though its SOL was trading at around 132.51 with short-term consolidation. Technical indicators give reason to think that it may trend towards $140, but focus is now more on presales developing core infrastructure than rallies based on price making.
Meme Coin Pressure Versus Utility Builds
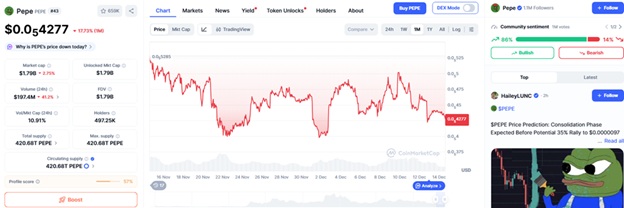
PEPE dropped to 0.000004276, or 17 percent a month, following a reoccurrence of fair-launch concerns. The fall highlights the inability of sentiment-based assets to perform in a time when liquidity constricts and transparency turns out to be the priority.
Top Presale Crypto LXYZ Emerges as the Infrastructure Leader
Top presale crypto LXYZ is adjusting itself to the middle of the Solana infrastructure wave by prioritizing the quality of execution over narrative momentum. Developed as a non-custodial, leveraged DEX, LXYZ applies a hybrid model of an AMM and an order book to combine liquidity into one meta-pool. The focus of this structure is on minimization of slippage and accelerated fills, which is in line with the institutional style expectations.
Source – SolidProof X
SpyWolf, QuillAudits and SolidProof have audited the protocol, confirming its emphasis on security and compliance with SPL. The presale (phase 1) is underway and the price of the token is 0.10 then 0.15 in the second phase. Many people already demand infrastructure-first designs, and the amount already raised is $111,000.

Why LXYZ Ranks as the Top Presale Crypto on Solana
The performance benefits of Solana enable LXYZ to execute leverage of up to 100x with a sub-400ms round trip, as well as to be completely on-chain and under the control of the DAO. Its unified liquidity model is the opposite of fragmented meme coin pools, which provides a more predictable trading environment. With the Firedancer upgrade of Solana nearing, the throughput of protocols such as LXYZ is set to increase in direct proportion to it.
The presale period provides visibility prior to subsequent repricing later in the life cycle (Phase 1 pricing still remains open). Buyers seeking audited utility over speculative trading are now considering LXYZ as a presale crypto to be listed early and high.
Conclusion
LXYZ is on the leading edge of the contemporary transition to audited and execution-driven infrastructure on Solana as market focus shifts away to meme-driven volatility. Phase 1 is live at $0.10 and has a definite roadmap, so early participation in the presale will provide an opportunity to enter before the prices increase.
For more information about LXYZ visit the links below:
Website: https://l.xyz/
Buy Presale- https://l.xyz/#sale
Twitter/X: https://x.com/ldotxyz
Telegram:https://t.me/ldotxyz / https://t.me/lxyzgroup






