BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, has not given up on its ambition to launch a spot Bitcoin?ETF in the US. The company has been in talks with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to address the regulator’s concerns and demonstrate the feasibility of such a product.
A spot Bitcoin?ETF would track the price of the underlying cryptocurrency directly, rather than relying on futures contracts or other derivatives. This would provide investors with a more transparent and cost-effective way to gain exposure to the digital asset class.
However, the SEC has been reluctant to approve any spot Bitcoin?ETF proposals, citing issues such as market manipulation, custody, liquidity, and investor protection. The regulator has repeatedly delayed or rejected applications from various firms, including VanEck, Valkyrie, and WisdomTree.
BlackRock, which already offers two funds that invest in Bitcoin futures, believes that it can overcome these challenges and convince the SEC to greenlight its spot Bitcoin?ETF. The company has been working closely with the regulator to address its questions and provide evidence of the maturity and robustness of the Bitcoin market.
According to sources familiar with the matter, BlackRock has presented data and analysis on various aspects of the Bitcoin ecosystem, such as price discovery, volatility, arbitrage, trading volume, and custody solutions. The company has also highlighted the benefits of a spot Bitcoin?ETF for investors, such as diversification, hedging, and innovation.
BlackRock is confident that its spot Bitcoin?ETF would meet the SEC’s standards and expectations and hopes to receive a positive response from the regulator soon. The company believes that a spot Bitcoin?ETF would be a game-changer for the crypto industry and would attract significant inflows from institutional and retail investors alike.
Franklin Templeton submitted an update for its spot Bitcoin ETF application.
Franklin Templeton, one of the world’s largest asset managers, has filed an amendment to its Bitcoin spot ETF application with the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The firm is seeking to launch the Franklin Templeton Bitcoin ETF, which would track the performance of Bitcoin based on the prices from selected spot exchanges. The ETF would not use derivatives or futures contracts, but rather hold Bitcoin directly in a custodial arrangement with NYDIG Trust Company.
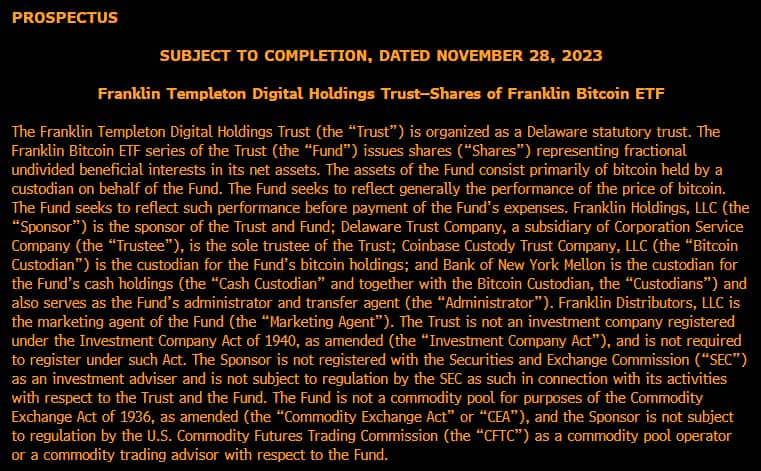
The amendment, submitted on November 29, 2023, provides additional details on the proposed ETF’s investment objective, strategy, risks, fees, and valuation methods. The document also outlines how the ETF would comply with the SEC’s requirements for investor protection, liquidity, transparency, and market integrity. According to the filing, the ETF would have a total annual operating expense ratio of 0.75%, which includes a management fee of 0.50% and other expenses of 0.25%. The ETF would trade on the NYSE Arca exchange under the ticker symbol FTBT.
The Franklin Templeton Bitcoin ETF is one of several spot Bitcoin ETF applications that are currently under review by the SEC. The regulator has not yet approved any such products in the US, despite growing demand from investors and increasing competition from other jurisdictions that have already authorized Bitcoin ETFs. The SEC has expressed concerns about the potential for fraud, manipulation, and volatility in the Bitcoin market, as well as the lack of reliable and consistent pricing data.
Franklin Templeton believes that its Bitcoin spot ETF would address these issues by using a robust methodology to select the spot exchanges that would provide the reference price for the ETF. The firm also claims that its custodial arrangement with NYDIG would ensure the security and safety of the Bitcoin holdings, as well as facilitate the creation and redemption of ETF shares.
Moreover, the firm argues that its Bitcoin spot ETF would offer investors a convenient and cost-effective way to gain exposure to Bitcoin without having to deal with the technical challenges of buying, storing, and transferring the digital asset.
The SEC has not yet announced a decision date for the Franklin Templeton Bitcoin ETF application, but it is expected to do so within 45 days of receiving the amendment. If approved, the Franklin Templeton Bitcoin ETF would be the first spot Bitcoin ETF in the US, and a major milestone for the crypto industry.






