Nothing is more important in a startup than having the capacity to acquire new customers, easily. In a network effect business, the most important product is “many users” because the more the users, the more useful the product becomes.
You need to know that in a perfect online market, the marginal cost of a digital product, under most scenarios, is zero. But markets are not perfect. And that means you must find ways to deliver great values to users even as the marginal cost tends to near zero. Why? Customers in the digital space congregate more into an ecosystem when the marginal cost is very low.
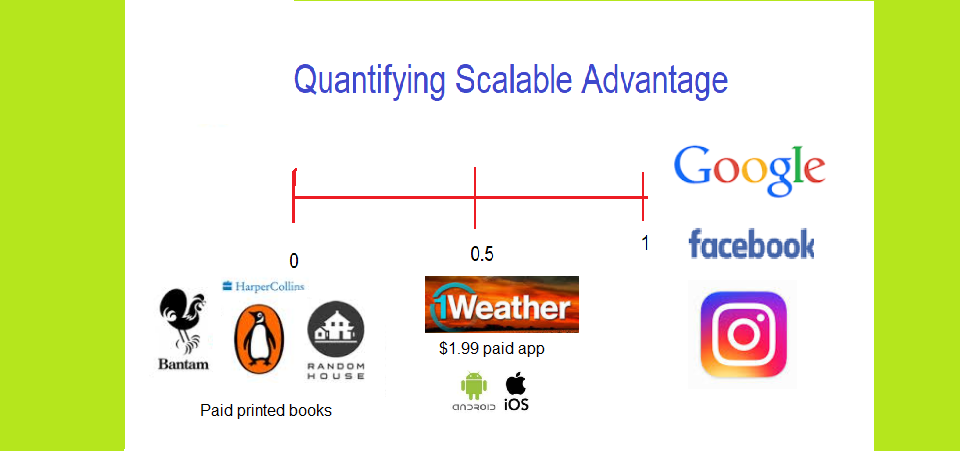
Scalable Advantage (SA) is a nexus with numbers between 0 and 1 which is used to ascertain the organic capacity to grow an enterprise, by examining the inherent elements like marginal cost and external forces, within an unconstrained and unbounded internet economy, where if nearly perfect, all transaction and distribution frictions between demand and supply disappear, producing an SA of “1”.
Today, I want to ask you: What is your Scalable Advantage? Does it get towards “1” or “0”? The trajectory will determine how far that business will go. I have a simple chart we developed in Tekedia Capital which we use to model the scalable advantages (hello mechanical advantage!) of startups. Here is one for some popular firms.
Comment on Feed
Comment 1: > within an unconstrained and unbounded internet economy, where if nearly perfect, all transaction and distribution frictions between demand and supply disappear
I’m curious about this. Google, Facebook, and Instagram seem to have low boundaries for non-paying users while presenting significant constraints and boundaries for paying users.
How does this intersect with SA as it relates to revenue growth?
My Response: You can use up to 98% of basic Google products for free. Those include Search and Gmail. The same applies when you look at Instagram and Facebook. In other words, since their cost is zero, barriers to use them are low. But even though they deliver them at zero point, the web is not a perfect market because the distribution cost (server cost, etc) is not zero. So, they need to make money to overcome the challenges of cost. Then comes advertising.
To drive that advertising, the goal is to scale more as that indeed means more revenue. In a way it works. The first 80% of users may deal with those costs while profits can come from the remaining 20% since within the system, the more users reduce your marginal cost over time. In other words, over time, it does not cost more per user to deliver services.
The implication is that profit can grow faster than revenue growth since the cost of servicing a user keeps going down due to scaling (even at limited revenue acceleration). You may check the video on click