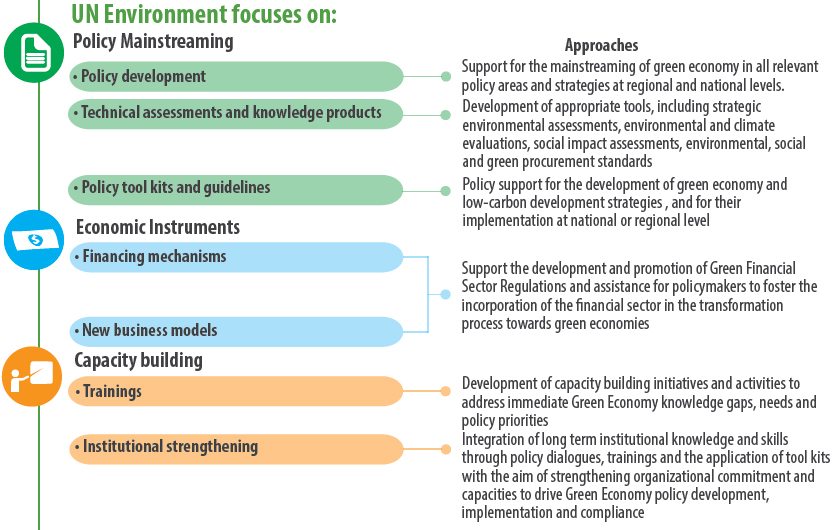
The concept of a green economy became popular as a response to the inability of neoclassical economics to effectively incorporate the value of natural resources and environmental degradation in market mechanisms. Global economic growth for the past half-century has been followed by quick environmental decline. Essentially, the economies of the world have, to date, over-depleted natural resources and severely devalued the ecological goods and services that comprise the basis of all economic activity.
Economic development has put great pressure on the natural resource base of the earth and the world is already resource drained. The consequences of climate change such as unpredictable weather patterns increased severity of natural disasters, and rearranged ecosystems, are already endangering food security and economic activities. Again, the prevalence of social and socio-political dissent and unrest, various social issues, and conflicts across the world are indirectly inspired by the inequitable sharing of limited resources that are unevenly distributed. A new development path is very necessary.
Green Economy and Sustainable Development: The Economic Impact of Innovation on Employment
There are numerous researches on the link between innovations for increasing productivity, where this connection is found to be very weak. This is linked to technological developments because of new machines. Truly, the importance of automation in terms of impact on employment has become vital. The employment impacts of innovation are a complicated mix of job displacement and compensation forces. The inquiry into the impact of innovation on employment is complex, as it involves a diverse conglomeration of effects. Strategically, product innovations and the introduction of new products leading to the creation of new markets can influence positive job-creation effects; while on the other hand, process or method innovations could lead to technological unemployment because of enhanced labor productivity.
Notwithstanding how threatening product innovations are, there is also a positive impact on employment, referred to as the ‘welfare effect’, though it can be enervated by a ‘substitution effect’ due to the displacement of mature products. Firstly, reduced production costs from a process innovation could cause a reduction in prices and this could trigger market demand by leading to more employment. However, this effect relies on the concept of perfect competition and demand elasticity, which can alienate the initial positive effect. Due to the more potential effects, as explained, the net impact of innovation on employment is complicated. Studies analyzing the impact of green innovations on employment are burgeoning due to the target of actualization of more sustainable development in most countries. However, the interest in green economy investments is peculiar given the need for government intervention to realize that new market opportunities could produce a lower return compared to other innovations.

Green Economy and Preservation of Biodiversity
There are many questions that economists ask relating to biodiversity including; is economic growth detrimental to biological diversity? Why will it likely turn out to be detrimental? How can the dangers be avoided? Etc. At a more individual level, the questions focus mostly on project analysis and specific environmental policy decisions. A distinctive characteristic of natural resources is that they are not immediately renewable; they can be selectively replenished only with time and subject to the limits of biological processes. Consequently, tapping these resources involves a compromise between instant benefits and future costs that relies on how the latter are considered relative to the former.
Economists have several interesting ideas of how the interest rate level, the result of the net benefit function and its outcome over time, and the variability of the resource’s inherent advance process contribute to the appropriate transitional path to exploitation. In effect, the process of sacrificing present consumption opportunities in favor of future generations should be a collective bargain. Both schools of thought suggest that the intertemporal allocations consequent of a decentralized market system may in essence be unfavorable to the present generation. Not only can the idea of conserving natural resources be a collective good, but the resources themselves are collective goods.
This is another major reason why overexploitation may occur. A third characteristic feature of several natural systems is the usually considerable degree of unpredictability of the future consequences of today’s preservation/depletion actions. This is partially a result of the intertemporal aspects of resource management but it is also the consequence of the enormous variability that is innate in natural systems.
There is are replete economic theories on how uncertainty can be incorporated into decisions made by private individuals or public policy framers. These theories target the implications of various forms of risk-averting actions for the optimal intention of resource preservation over time. Implementing these theories, however, needs empirical estimations of the type of risk preferences preferred by the decision-makers, in the terms of positive analysis, or value determinations about the type of approach to decisions on the risk that can be adopted, in the case of normative analysis.
Environmental economists are interested in markets because they are interested in estimating the choices of individuals and verifying their compromises connecting environmental resources and money or standard market products. Both direct and indirect methods for measuring the preferences of individuals have been greatly honed in recent years.
Emerging Opportunities
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) represent the most ambitious development agenda ever, determining the vision, blueprint, and goals for the evolution to a sustainable society. With just over a decade left to realize the SDGs, a major effort is needed to produce results.
Challenges remain to bring these trends to fruition. First, most of today’s green market expansion is focused on a limited number of developed and emerging economies, with a necessity to diversify the geography of green solutions, with the least struggling countries.
The Middle East with the North African region are good illustrations, so far the earth’s most water-deficient and food import reliant region, also having temperatures increasing faster than the global average. Without partnerships and finance expansions in the years ahead, trends of poverty, displacement, and fragility will increase.
The UNDP, UN Environment, UNISDR, UN Habitat and WFP are launching a new SDG Climate Facility regional plan to take action on these issues; a regional initiative in conjunction with the League of Arab States, the Arab Water Council, and other partner countries.
With the SDG Climate Facility, the UN will assist country partners to identify opportunities to mainstream green solutions into national financial structures, the rules and framework governing the banking sector, investment, insurance, capital markets, and other segments of national financial systems necessary to green market development, and actualize a directional estimate of the investment gap enroute 2030.
A focus will also be on innovation, to establish new green investment options among public and private partners in order for scaled-up climate finance to be applied in a way that profits the poorest and most vulnerable in society, including crisis-ridden communities.
Shifting to a Green Economy
Actualizing the full potential of green jobs is predicated on countries assuming their roles in developing the green economy and formulating policies that will foster investment. The current model has proven to be ineffective and inoperable, not only for the environment but for economies as a whole. There is an urgent need to move to a sustainable development path with an implementable set of policies, with people and the planet at the focus.
Claims that the greening industry would lead to job losses, because of the changes to some traditional industries such as fossil fuel extraction have been countered by the argument that environmental sustainability is not a job killer, as always assumed. In contrast, if properly supervised, the result can be more and improved jobs, poverty alleviation, and social incorporation.
Though some areas like fishing fleets are more vulnerable to losses lasting durable conduct could prevent job losses. For illustration, an evaluation suggests that one million workers in Asia could have lost their livelihoods in forestry because of poor resource management, which could have been largely prevented with better policies and implementation. Jobs easily identified as “green” are not the only ones to be affected by the transition to a more environmentally sustainable economy.
Some of the sectors identified as being most impacted by the changes include agriculture, energy, resource-intensive manufacturing, fishing, building, and transport. Women could benefit if the transition is properly implemented as it could provide them with increased access to jobs and sizeable incomes.
Green Economy Offer for Developing Countries
To be beneficial to develop countries, green growth should be reconciled with the two strategic features of natural resource harvesting and poverty in these countries. First, primary products form most of their export income, also they are incapable of diversifying from basic production. Again, numerous economies experience a considerable portion of their rural population resident on less non-arable agricultural land and in inaccessible areas, thus supporting subsistence. If green growth is capable of speeding up an economy-wide transformation and poverty alleviation in struggling economies, then it must be followed by policies targeted at overcoming the two strategic features of natural resource harvesting and poverty. Policies and reforms must foster synergistic linkages of primary production, improve its incorporation with the other dimensions of the economy, and elicit opportunities for creativity. Rural poverty, notably the constant concentration of the rural underprivileged on agricultural lands that are difficult to cultivate and in inaccessible areas, needs to be looked into by more targeted policies and investments, and where possible, policies to encourage rural-urban migration.
Action Indicators of a Green Economy
Admittedly, in recent years there have been many attempts to create indicators and assessment frameworks that address the environmental and social aspects of progress. Additionally, there has been an increasing realization of the limitations of GDP, notwithstanding the fact that it is still widely deployed today as an indicator of social welfare. Agreeing on the best alternative sustainability indicators is highly complex, notably as a result of the intricacies of how to balance our environmental, social, and economic goals still being a matter in contention. However, notwithstanding the fact that they are still unable to achieve the same level of impact as GDP, other indicators and alternative measurement theories are slowly being infused into the policy-making process. Still, there has been palpable scientific progress in assessing various dimensions of sustainability that have not yet been explored by policymakers.
CONCLUSION
Sustainable development has assumed a multi-dimensional and complex approach with many different characterizations and measurement approaches. A plethora of researches has been targeted towards the development of indicators in this area, consequent to a jungle and often complicated, available indicators. There are numerous indicator sets currently present in the field of sustainability, though in practice only a limited number of them find their path into the policy-making process. In years ahead the incorporation of green economy and sustainable development in the policy process will burgeon as a result of the growing recognition of the limitations of GDP as a measure of welfare. Rather than focusing only on developing the perfect indicator or set of indicators, it is more useful to educate the public in the use of indices, due to the fact that virtually any standard can furnish useful indicators for some political inquiry and misleading messages for others.
Like this:
Like Loading...