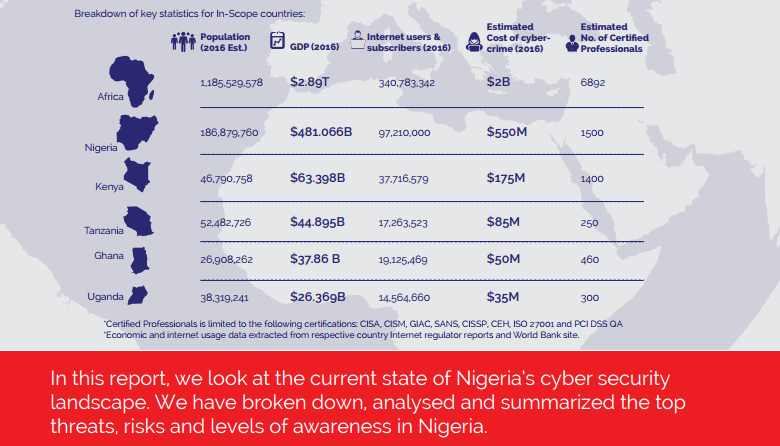
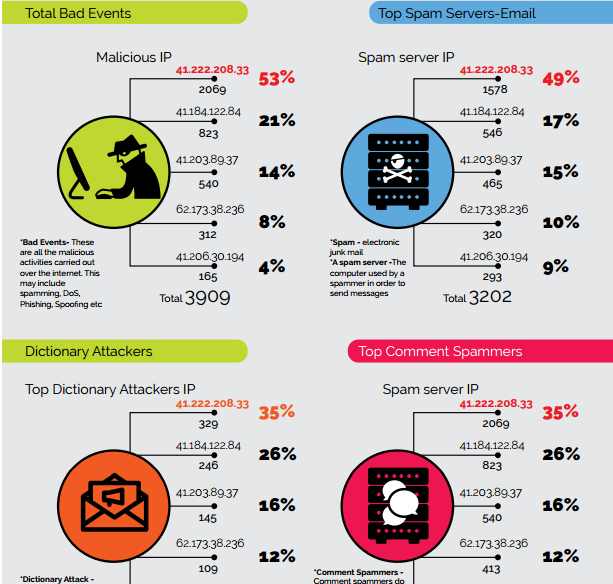
We are offering limited scholarships on our Nanodegree programs at First Atlantic Cybersecurity Institute to African students. This is a $2,000 value scholarship covering our Certificate and Diploma programs which are prerequisites to our Nanodegree programs. Free broadband internet access is also available for Nigerian students.
First Atlantic Cybersecurity Institute (Facyber) is a cybersecurity training, consulting and research company specializing in all areas of cybersecurity including Cybersecurity Policy, Management, Technology, Intelligence and Digital Forensics. Facyber is based in United States.
The clientele base covers universities, polytechnics, colleges of education, governments, government labs and agencies, businesses, civil organizations, and individuals. Specifically, the online courses are designed for the needs of learners of any discipline or field (science, engineering, law, policy, business, etc) with the components covering policy, management, and technology.
Structure
Programs are structured as Certificate, Diploma and Nanodegree programs with deep resources to support Learners. Please see complete Facyber catalog and detailed Table of Contents.
Learn about
– Cybersecurity Policy (Certificate, Diploma, or Nanodegree)
– Cybersecurity Management (Certificate, Diploma, or Nanodegree)
– Cybersecurity Technology (Certificate, Diploma, or Nanodegree)
– Cybersecurity Intelligence and Digital Forensics (Certificate, Diploma, or Nanodegree)
Our Cybersecurity education is structured around four key pillars of policy, management, technology and digital forensics. This implies that we cover all the core needs of any organization or state institutions. While some staff like corporate lawyers may require training on policy, some staff like IT managers may need technical skills. Others like business leaders will find the management module useful. We deliver all these programs through our web portal . The program structure is presented below: certificate programs take 12 weeks; diploma programs which require certificate programs as perquisites take 24 weeks (inclusive of the certificate programs) and the nanodegree programs require a live (virtual) one week training with the diploma programs as prerequisites
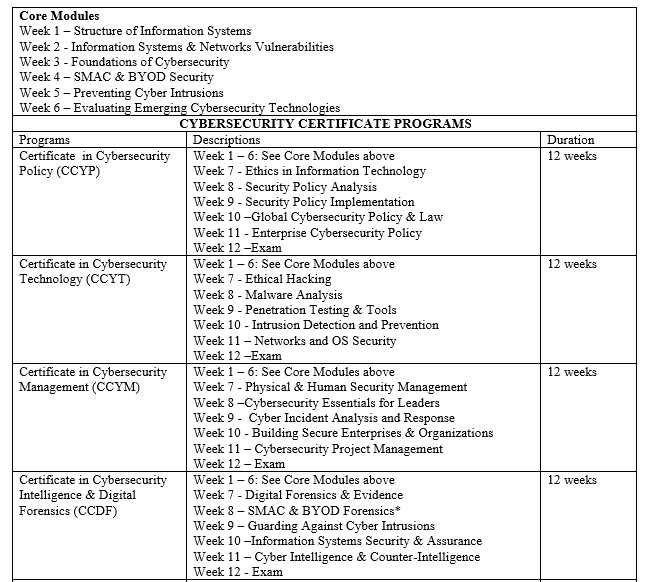
Program Descriptions
- Certificate in Cybersecurity Policy (CCYP): Certificate in Cybersecurity Policy deals with the policy analysis and implementation aspects of cybersecurity. It presents theory and topical issues, at government and enterprise levels, with both technical and managerial components in the fields of information systems security. The program helps learners develop skills on the policy, ethical, and legal issues associated with cybersecurity and information security.
- Diploma in Cybersecurity Policy (DCYP) Capstone: This is a practical-oriented program where learners are tasked with developing solutions for a theoretical or real case cybersecurity policy issue with the guidance of a mentor. A project report is required at the end of the program.
- Certificate in Cybersecurity Technology (CCYT): The Certificate in Cybersecurity Technology is designed to provide learners with skills to analyze multi-faceted complex cybersecurity issues, develop capabilities to make strategic decisions to protect organizations from threats and become competent cybersecurity professionals.
- Diploma in Cybersecurity Technology (DCYT) Capstone: This is a practical-oriented program where learners are tasked with developing capabilities in the core technical aspect of cybersecurity. Learners will have access to some tools and equipment to work throughout this program. A project report is required at the end of the program.
- Certificate in Cybersecurity Management (CCYM): The Certificate in Cybersecurity Management equips and prepares learners with modern skills to become effective managers across the broad nexus of cybersecurity and intrusion preventions in organizations. The central core is developing capacity to prevent anticipated cyber intrusions, using experiences to mitigate future threats, and formulating and implementing enterprise-level cybersecurity roadmaps. The program also explores the roles of regulation, policy developments, legal instruments and civil liberties.
- Diploma in Cybersecurity Management (DCYM) Capstone: This is a practical-oriented program where learners are tasked with developing cybersecurity project management capabilities with the guidance of a mentor. Here, learners develop cybersecurity implementation frameworks. A project report is required at the end of the program.
- Certificate in Cybersecurity Intelligence & Digital Forensics (CCDF): The Certificate in Cybersecurity Intelligence & Digital Forensics is structured to provide modern skills to those interested in digital forensics, digital intelligence and uncovering digital evidence. The program equips learners with broad analytical frameworks and prepares them to become competent cyber investigators.
- Diploma in Cybersecurity Intelligence & Digital Forensics (DCDF) Capstone: This is a practical-oriented program where learners are tasked with developing capabilities in digital forensics, digital evidence and digital intelligence. Learners will have access to some tools and equipment to work throughout this program. A project report is required at the end of the program.
Applications
To apply, you need to get a letter from your HOD or Dean indicating that you are a current student in an African university. Send that along with your resume to info@facyber.com and cc audrey.kumar@milonics.com . In a cover letter, explain why Facyber should offer you a scholarship for our Nanogree program, priced at $2000. This program will take 24 weeks since the students selected will automatically be accepted in the Certificate and Diploma programs which are prerequisites to the nanodegree programs.

Free Broadband Internet
If you are in Owerri (Nigeria), we are making our office available for students who want to enroll in our programs but have limited access to internet. If you do enroll, not necessarily via this scholarship, we welcome you to 124A Okigwe Road, Owerri. There, you will have access to our programs at no extra broadband cost. This broadband service is supported by Fasmicro, our Nigeria office.
Deadline: March 31 2017
info@facyber.com