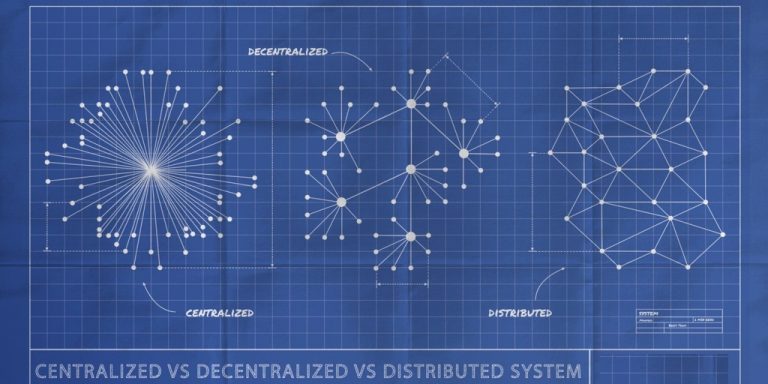
Decentralization is a system in which lower-level components operate on local information to accomplish global goals, without a central authority or controller. In contrast, a centralized system is one in which a central entity exercises control over the lower-level components, either directly or through a power hierarchy.
Decentralized systems have many advantages over centralized systems, such as failure tolerance, redundancy, scalability, and autonomy. For example, the Internet is a decentralized system that allows users to communicate and share information across the world, without relying on a single server or authority. However, decentralized systems also have some challenges, such as management complexity, security risks, and coordination difficulties.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest and demand for decentralized systems in various domains, such as computing, information technology, economics, and governance. One of the main drivers of this trend is the emergence of blockchain technologies, such as those used in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Register for Tekedia Mini-MBA edition 18 (Sep 15 – Dec 6, 2025) today for early bird discounts. Do annual for access to Blucera.com.
Tekedia AI in Business Masterclass opens registrations.
Join Tekedia Capital Syndicate and co-invest in great global startups.
Register for Tekedia AI Lab: From Technical Design to Deployment.
Blockchain technologies use cryptography and consensus algorithms to create a distributed ledger of transactions that is verifiable and immutable, without the need for a centralized intermediary or authority. This enables new possibilities for peer-to-peer transactions, smart contracts, digital assets, and decentralized applications.
Another reason for the world push for decentralized systems is the increasing awareness and concern about the drawbacks and dangers of centralization. Centralization can lead to inefficiency, corruption, censorship, surveillance, and abuse of power by the central entity or authority.
For instance, many people are dissatisfied with the centralization of social media platforms, which can manipulate user data, influence public opinion, and censor content that they deem inappropriate or harmful. Decentralized systems can offer more privacy, freedom, and control to the users, by allowing them to choose their own rules and preferences.
Decentralization has some challenges and limitations, some of these include:
Management complexity and coordination: Decentralized systems require more effort and resources to manage and coordinate the components, especially when they are large and diverse. This also increases the risk of conflicts and inconsistencies among the components.
Quality assurance and accountability: Decentralized systems may lack standards and regulations to ensure the quality and reliability of the components. This also makes it harder to monitor and evaluate the performance and behavior of the components, as well as to enforce rules and sanctions.
Scalability and efficiency: Decentralized systems may face difficulties in scaling up or down to meet changing demands and conditions. This also affects the speed and cost of the system, as well as its environmental impact.
Therefore, decentralized systems are not a panacea or a one-size-fits-all solution. They need to be carefully designed and implemented according to the specific context and objectives of each domain and application. They also need to be balanced with centralized systems when appropriate, to optimize their strengths and mitigate their weaknesses.
In conclusion, decentralized systems are systems that operate on local information to achieve global goals, without a central authority or controller. They have many benefits over centralized systems, such as failure tolerance, redundancy, scalability, and autonomy. They also address some of the problems and challenges of centralization, such as inefficiency, corruption, censorship, surveillance, and abuse of power.



