This chapter will introduce the reader to 5G cellular generation network, cover its widespread applications within different industries (verticals) and highlight some ethical impact of 5G and emerging technologies on society.
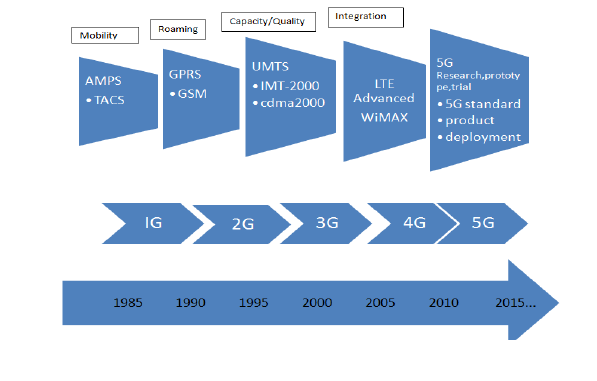
5G refers to the Fifth Generation Cellular Network. Every ten years, there is always a shift from previous generation onto a newer generation, as depicted in Fig. 1.1 below.
Register for Tekedia Mini-MBA edition 18 (Sep 15 – Dec 6, 2025) today for early bird discounts. Do annual for access to Blucera.com.
Tekedia AI in Business Masterclass opens registrations.
Join Tekedia Capital Syndicate and co-invest in great global startups.
Register for Tekedia AI Lab: From Technical Design to Deployment.
1.1 What is 5G?
It is a newer generation which presents different opportunities to different stakeholders depending on where your interests lie. To an equipment vendor like Ericsson, 5G represents a market opportunity to drum up the sales of infrastructures like small cells etc. To an academic, 5G would provide an opportunity to solve complex research problems within the Communications Industry.
To a car manufacturer, 5G simply represents the opportunity to make revenues from new offerings like connected cars. To a regulator, 5G would lead to the opportunity to make increased profits from new spectrum release and lots of debate on band issues etc. To telcos, it may represent a way to increase revenue, consider new offerings (verticals) and address the increased competition from over the top (OTTs) applications like WhatsApp etc.
For the technology media, it’s an opportunity to increase subscription audience and perhaps pitch the development and deployment of 5G as a race between countries or operators.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has classified 5G in terms of three use-cases presented below:
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband: It is simply an extension of 4G and promises a speed of 10/20Gbps for either your uplink/downlink. In literal terms, as a user, you should be able to download an HD film in seconds [7].
- Ultra-Reliable and Low latency: Here, a stringent requirement of less than a milli-sec of delay is anticipated for applications like autonomous driving and remote surgery e.g. imagine a robot performing a surgery operation during an emergency, a delay could have damning consequence [7]
- Machine to Machine type Communications: allow for IoT based applications, 10^6 devices per km^2 e.g. smart metering, smart city, smart agriculture etc. [7]
1.2 Applications of 5G
5G will be a major technology in growing industrial digitization applications. For example,
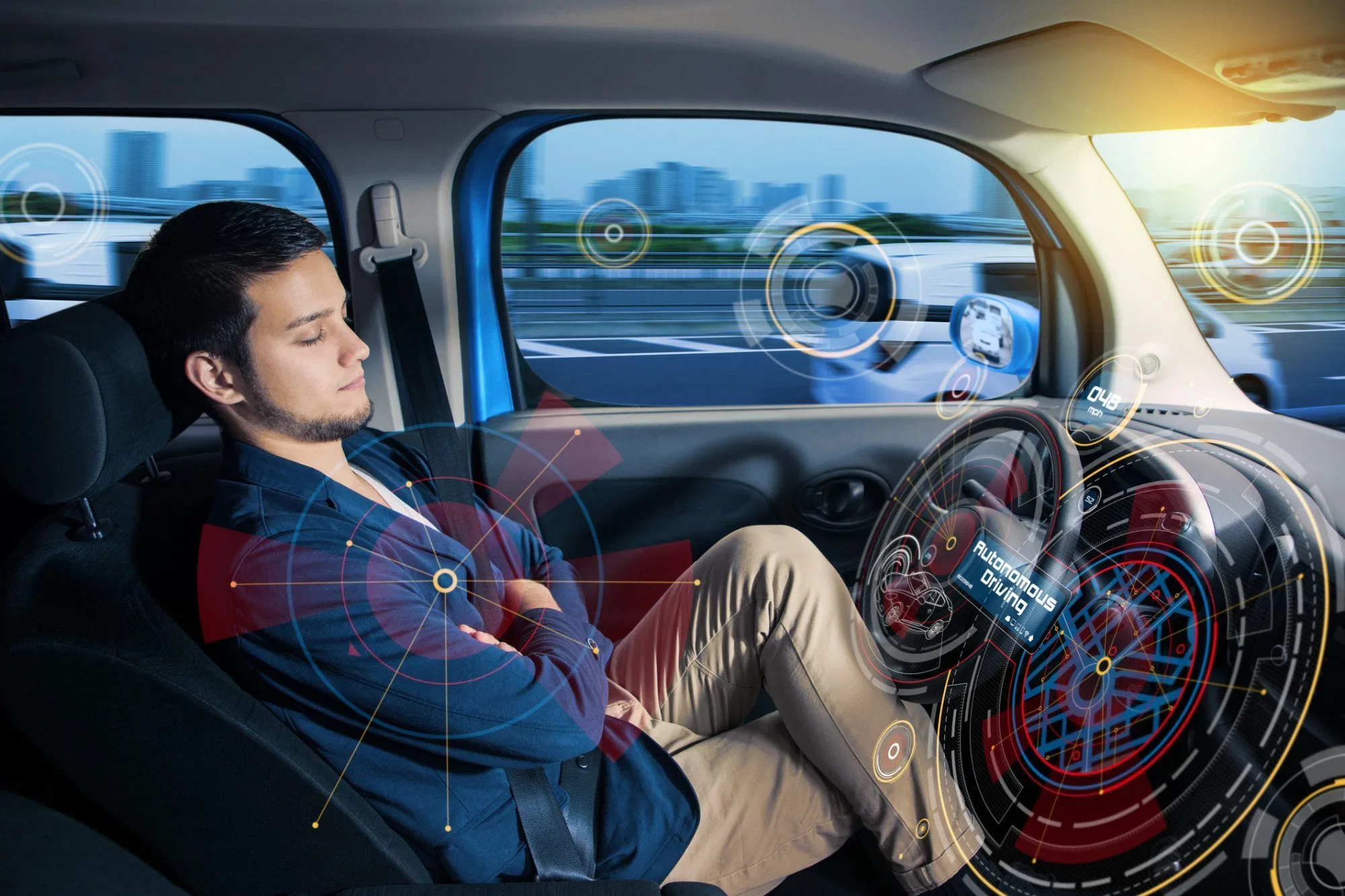

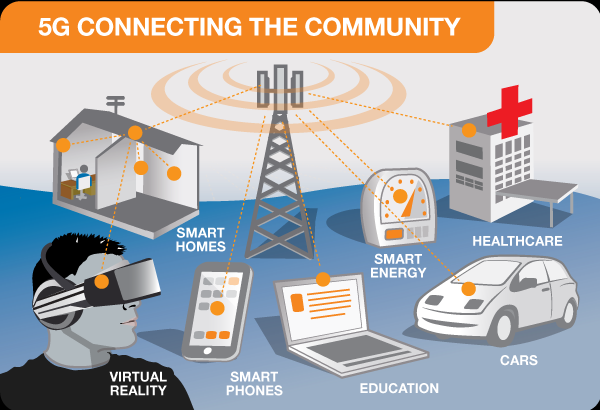
- Transportation System: Autonomous cars will revolutionise transportation (see Fig. 1.3 below) which would reduce commute time, allow passengers to concentrate on other tasks and reduce accident due to human error [2].
- Smart Cities: Highly Efficient Transport Systems would therefore lead to the development of smart cities where for example, connected sensors can help in determining the water level of a city and predict when and whether a city will be flooded or otherwise [3]. Connected sensors can also help direct passengers to the nearest parking spaces with available facilities [4].
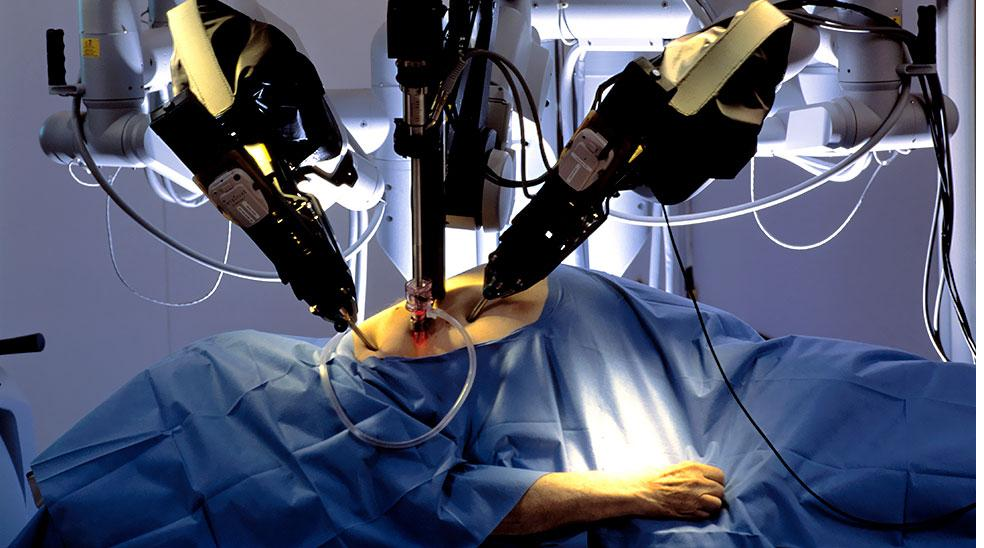
- Health Care: Internet of skills alongside remote surgery can help to improve health care in developing as well as developed countries. For instance, a surgeon in remote Africa can perform complex surgical procedures through video access to the best surgeon in the world. Robots can be made to perform precise and complex surgical operations thereby reducing the death rate from human error, as depicted in Fig. 1.4 below. 5G will also aid the remote monitoring of patients who need mobility assistance or are residing far away from hospitals or clinics. Drones can also be used to deliver drugs in remote places in developing countries e.g. this is already happening in Malawi, Ghana etc. [5].
- Package Delivery: Amazon is already testing the use of drones to deliver its packages in the US, as depicted in Fig. 1.5 below. This is particularly useful in rural or remote areas, where it takes a significant amount of time for packages to arrive using the current system.

Figure 1.5: Drone delivering an Amazon package [24]
- Industry 4.0: The use of robots, automated machines and sensors etc. would lead to Industry 4.0 which would bring about the development of highly automated and efficient factories and industries. Machines in factories can therefore be programmed to order for maintenance support and spare parts through the use of automated sensors.
- Smart Agriculture: Food production can be increased through smart agricultural initiatives like the use of sensors to predict the right level of water and fertilizer to apply to different parts of the farm [6].
Livestock management can be enhanced through the use of connected sensors monitoring the welfare of the animals. Robots can be employed to harvest and perform farming operations. Farmers and Buyers can be connected through Artificial Intelligent System, thereby reducing food wastage. Weather conditions can also be predicted for agricultural processes using Big Data [5].

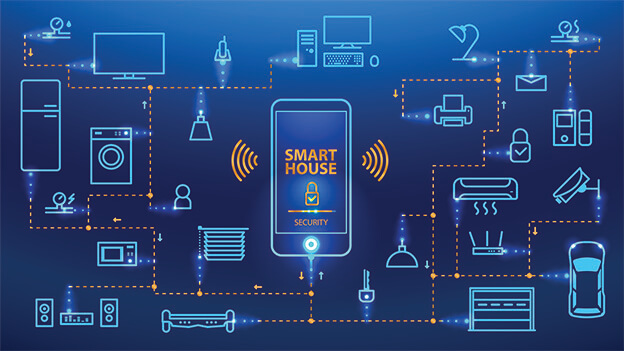
- Smart Home: Homes can be made smarter through smart energy and other smart homes applications, for example, one can programme a refrigerator to order groceries online when exhausted, see Fig. 1.6 above. Smart energy can help in reducing the energy consumption within the home.
- Future of Work: Labour force need not be restricted to a geographic location through smart educational initiatives and internet of skills.
- Fintech: Mobile money and other electronic bank transactions would make bank transactions faster which would make life easier.
- E-commerce: Consumers are able to purchase products and services from any geographic location as we are already witnessing.
- Education: Robots can serve as educational Instructors and has huge implications for developing countries where there is a shortage of such professionals [5].
1.3 Ethical Implication of 5G
It is very clear from the foregoing that 5G, alongside other emerging technologies, would lead to a disruption in all parts of the Society. For example, certain jobs will no longer be available as robots will replace humans. This will of course engage ethical questions like:
- Should robots have the same rights as humans?
- Should robots be taxed for every job they replace?
- If robots can think and have emotions, what would then make us human?
- How do we ensure that there are no security breaches in our digitally interconnected world?
- How do we ensure that data theft and privacy concerns are respected in the wake of fake news, terrorism, profiling of individuals?
- How do we protect the society from the use of autonomous weapons?
- Will these technologies widen or reduce the existing inequalities within the world?
- Will these technologies reduce or increase the gender bias or the digital divide within the world?
These and more questions need to be addressed so that the benefits of these technologies can be maximized whilst minimizing the risks [5].
Back to Table of Contents.



