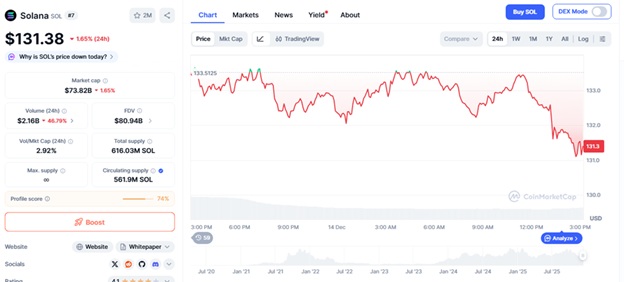
Crypto markets are stable with Bitcoin at about $90,057 and Ethereum at about $3,110, and institutional demand is moving to Solana and the overall activity of DeFi. The cooperation of the Sei Network with the world-famous smartphone manufacturer Xiaomi can be seen as a significant breakthrough that paves the way to mainstream blockchain access.
Sei says that under this deal all new Xiaomi smartphones sold outside the United States and mainland China will have its next-generation crypto wallet and discovery app installed by default in 2026. The integration offers instant access to Web3 applications and payment options through Google account or Xiaomi account logins, decreasing the onboarding friction of more mainstream users. The launch will focus on high-adoption markets such as Europe, Latin America, Southeast Asia and Africa where Xiaomi has a substantial market share. This partnership is also entailed with a 5M Global Mobile Innovation Program to assist mobile blockchain application and further enhancement of stablecoin payments at more than 20,000 retail outlets. These characteristics bring blockchain technologies nearer to regular consumers and may lead to wider usage by non-traditional crypto followers.
This collaboration is important as integrating a crypto wallet into consumer devices will skip the complexity of downloads and onboarding obstacles, introducing a default point of access to decentralized applications and payments. The project has the potential to increase on-chain activity and expand market participation, especially in third world nations where mobile connectivity leads to digital usage, through direct connectivity of blockchains to commonly used hardware. These cross-industry integrations are defining a new era of user acquisition and the useful application of crypto.
LXYZ – Leading the Charge as a Top Presale Crypto
LXYZ is the leader in presale crypto with its unique design, that appeals to professional traders and the performance of institutional quality in the high-speed network of Solana. The stage 1 price at $0.10 has been developing towards an increase of 0.15 at the next stage, and hopefulness is increasing concerning its development pattern. Early investor confidence is already indicated by the fact that the presale has already raised over $111, 000 in total.
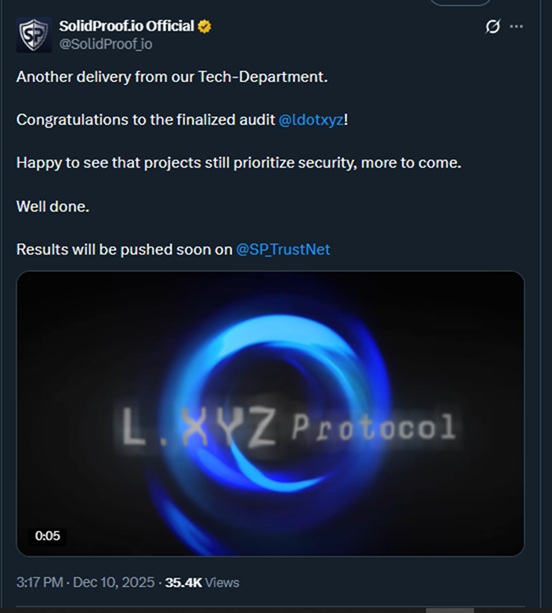
Source – SolidProof X
The architecture of LXYZ is based on deep pooled liquidity and reduction of slippage, which has made it an efficient spot and futures trading leverage trading environment. Its meta-pool and vAMM architecture is capable of high throughput and competitive execution costs, more than 90 times better than standard on-chain liquidity wrappers. LXYZ has good foundations in security and contract integrity, audited by SpyWolf, QuillAudits and SolidProof . Being a cross-chain settlement hub and trading platform with more sophisticated features, LXYZ stands to seize capital shifting away off-the-shelf to new Solana activities.
Why LXYZ Claims a Top Spot Among Presale Crypto Projects
The price structure, i.e., the price of LXYZ is currently at $0.10 in phase 1 and has a next tier of $0.15, but its architecture, which allows 100x leverage trading opportunities and professional types of orders on a decentralized market, is worthy of note. LXYZ is symbolic of the increased community engagement and commitment to liquidity with 1,101+ holders already staking tokens as part of the presale dynamics.
The project uses Rust/Anchor contracts that are performance and safety-friendly, and triple audits of SpyWolf, QuillAudits, and SolidProof make the project less risky to early adopters compared to technical risk. LXYZ is perceived as a viable competitor of consistent growth by market analysts following other Solana-based innovations because of its liquidity pooling cross-chain, mobile accessibility, and comparative fees. Potential investors with leading presale crypto positions could find LXYZ as a good position to enter before the ecosystem grows further.
Conclusion – Secure Your LXYZ Position Before the Next Leg Up
As the macro crypto markets stabilize, and institutional flows are diversified into Solana-type levels of innovation, projects such as LXYZ are a promising top presale crypto entry before the 3-4 orders scale to wider liquidity access. Its highly vetted contracts, sophisticated trading, and high presale parameters, with a price of $0.10 and a subsequent phase of 0.15, are what make it a project worth considering today. Get into the LXYZ presale early to place yourself ahead of the potential growth with Solana gaining momentum.
For more information about LXYZ visit the links below:
Website: https://l.xyz/
Buy Presale- https://l.xyz/#sale
Twitter/X: https://x.com/ldotxyz
Telegram:https://t.me/ldotxyz / https://t.me/lxyzgroup