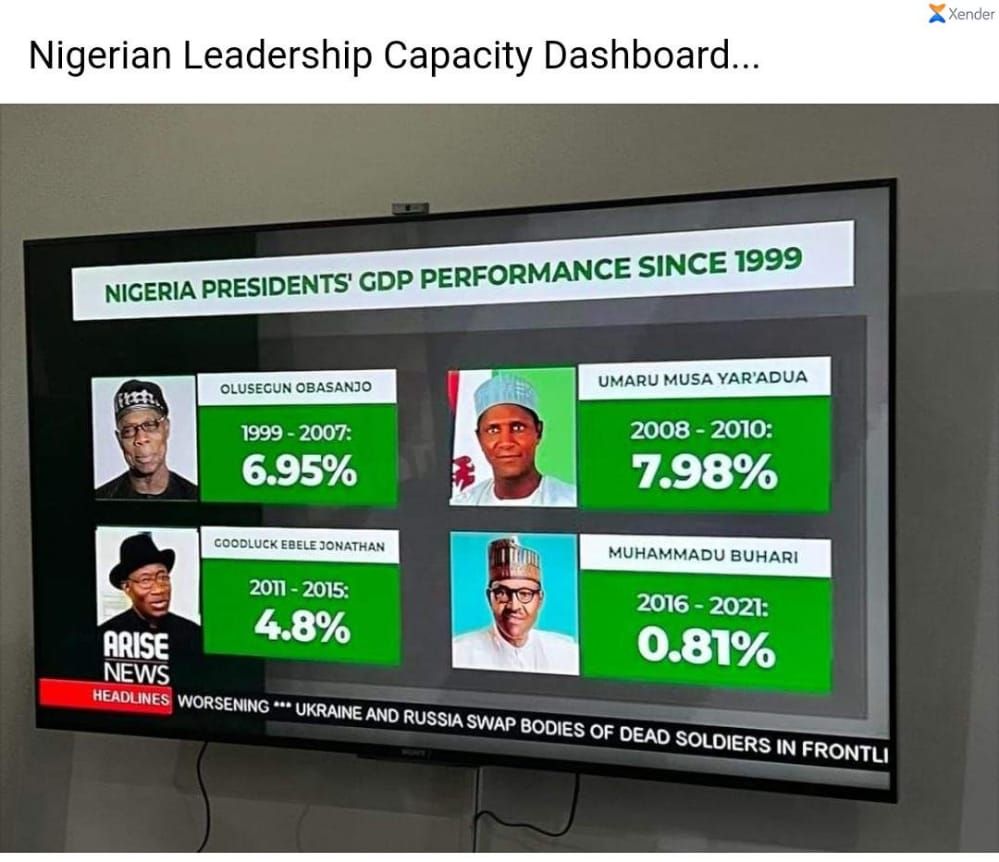
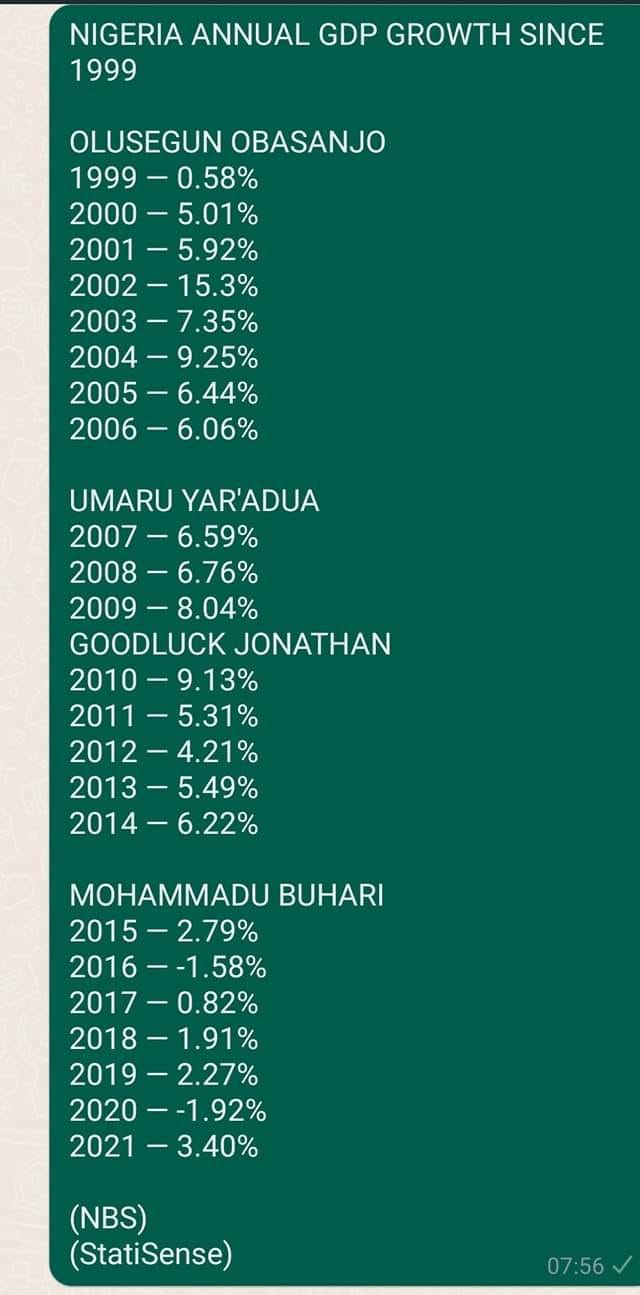
The “Indiyawan Kano” (The Indians of Kano) Narrative is not a common one, as the situation remains rather fluid.
I start off this article by drawing from a book “Nigerian Film Culture and the Idea of the Nation: Nollywood and National Narration,” edited by Professor James Tar Tsaaior and Professor Françoise Ugochukwu, which posits that Nollywood, “the Nigerian video film text, is deeply rooted in the sub-soil of its social and cultural milieux.”
It further argues that the genre is “engaged in the relentless negotiation and re-negotiation of the everyday lives of the people against the backdrop of their cultural traditions, social contradictions and the politics of their ethnic/national identity, longing and belonging.”
Featuring a range of essays, there is a further claim that the contributions “weave an intricate and delicate argument about the critical role of Nollywood to the idea of nationhood and the logic of its narration with implications for language, politics and culture in Africa.”
Setting the Scene
Yusuf Baba Gar’s investigation of “Folktales in Kannywood Videos” interrogated the storylines in Kannywood (the film industry in Kano, the commercial nerve centre of northern Nigeria) videos, and highlighted how cultures can transcend geographies through film and folktales. It also speaks to the never-ending debate around migration, migrants and acculturation of settlers in a host context. Interestingly the intercultural integration and amalgam of cultures as something that is not much envisaged.
Disaggregating, Kannywood from the broader Nollywood, he draws attention to a growing crop of actors/actresses described as the “Indiyawan Kano” (The Indians of Kano). Yes, you heard/ read right – the Indians of Kano.
Therefore, when we talk about the arguably Big Three – Hollywood, Bollywood and Nollywood, we need to pause and reflect upon this study, which provides some interesting insights into some recent interactions and alliances. As the study challenges “the initial criticism that the videos are mere adaptations of Bollywood.”
Adaptations of Bollywood may be putting it mildly considering what has been denounced as a “Menace of Appropriation” of Bollywood by Kannywood. Let me explain drawing further insight from three articles.
First, the study by Professor Muhammad Muhsin Ibrahim of the Institute of African Studies and Egyptology University of Cologne entitled “Kannywood and the ‘Menace’ of Appropriation of Romantic Movies,” echoes this view. As Professor Muhsin points out about his article:
“This paper is set out to discuss this issue through a content analysis of a recent film titled Sareena (2019, dir. Ali Nuhu). The movie, released early this year (2019), is not only a bloated, implausible melodrama but also a direct mimicry of a famous Indian film, Kaabil (2017, dir. Sanjay Gupta).”
Second, the study by Professor Abdalla Uba Adamu of the Bayero University, Kano on ‘Currying favour: eastern media influences and the Hausa video film’, confirms this ‘new’ narrative. Indeed, the professor has more recently written about “The Linguistic Domestication of Indian Films in the Hausa Language,” and all the red flags being raised. Citing prominent scholars in this research area such as Professor Adamu, Muhsin highlighted how Hindi (arguably Bollywood) films have been appropriated in Hausa from songs (e.g., So Bayan Ki) to storyline (e.g., Ciwon Ido, Burin Zuciya and Zo Mu Zauna), and even choreography (Zabari).
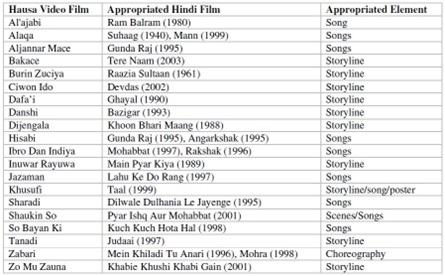
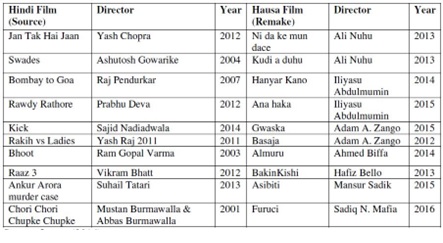
Third, and moving away from the scholarly discourse (for the time being at least), one article entitled “Move over India: How Bollywood conquered Nigeria,” published by Asia by Africa, in February 2018 points out, “originally, a cheap alternative to Western films, Bollywood’s themes and stories resonated with Nigerians turning an import gamble into a national obsession. From literature to music to filmmaking, Bollywood has had an indelible impact on Nigerian culture.”
Evidently, Nollywood, and it’s Nigeria audience, have been obsessed with Bollywood for over six decades, and this obsession has been captured in this third article, which places the country as “one of the Indian film industry’s best export markets.” The history dates back to the 1950s, a period that coincides with the pastime of Lebanese immigrants in the country. With screening popping up almost any or everywhere – from open-air courtyards and impromptu movie houses, especially in northern Nigeria.
Breaking down barriers
Other interesting cultural barriers seem to have been negotiated, and navigated, because of the prolonged interactions of both cultures. The first is the language barrier issue, and a second is cultural bonding. Starting with the language barrier issue, it has been reported, “many people re-watched the same movies dozens of times, eventually learning snippets of Hindi in the process.” The argument remains that, “while Nigerian audiences could not understand the dialogue, the pacing and plot of films nevertheless enabled them to figure out the stories. For instance, the three hour long, 1957 classic Mother India remains one of the most popular Bollywood films of all time in Nigeria.”
A recap of the highlights:
- Originally, a cost-saving gamble, Bollywood’s introduction into Nigeria in the 1950s evolved into a cult following in subsequent decades.
- The Bollywood craze hit new heights in the 1970s and 1980s. Afterwards local films began to supplant Indian ones – with the emergence of Nollywood.
- The resurgence of Bollywood in recent years is due to Indian studios outpacing their Nigerian counterparts in terms of production quality and This makes some nervous that Bollywood could spell Nollywood’s demise, while others maintain that Nollywood should focus on quality, not quantity, in order to regain market share.
- Throughout Nigeria, informal movie venues showing Indian films regularly sell out, buoyed by the support of loyal fans “singing along in Hindi” despite not speaking the language.
- In the 2012 film U.D.E. became the first co-production between Nigeria (Chukwuma Osakwe, director) and India (Parveen Kurma, assistant director). The two co-stars make a fitting metaphor for the ties between the two film industries, with Lavina Qureshi playing the Indian love interest of Nigeria’s Daniel Lloyd.
- Set in Lagos and Chandigarh (Punjab), the movie deals with the same cross-cultural themes that made Bollywood resonate in Nigeria e.g. religion, visa denials by western countries and the challenges faced by young people, thereby, creating a loyal audience in Nigeria.
- In January 2015, India’s high commissioner to Nigeria announced that India would facilitate a partnership between the Nigerian and Indian film industries.
- In 2015 Nigerian-Indian actor Aivboraye Lawrence Osagie became the first Nigerian to feature in a Bollywood film, Love is an Illusion.
- An example of Bollywood’s international success and ease with which it has surmounted language barriers comes in the form of a 2015 video showing Miss Nigeria and Miss Indonesia bonding over their shared love of Bollywood films, before breaking into a song.
- In January 2016, Emem Isong (Nigeria filmmaker) created Love is in the Air, a romantic comedy starring popular actors from both Nollywood and Bollywood.
- Lagos’ Indian Festival in 2016 also saw film industry cross-promotion, with the Indian embassy and Lagos city displaying the best of the best of Indian and Nigerian cinema.
- As one report puts it, “perhaps the most meta example of the cross-pollination between Nigerian and Indian film has been the 2017 Nollywood movie ZeeWorld Madness, a comedy that pokes fun at the Nigerian obsession with the ZeeWorld Bollywood movie channel on DSTV.”
In the light of the above, perhaps it may well be time to reconsider the posturing of one Prince Bubacarr Sankanu, a scholar on African cinema, and founder of a think-tank on African cinema, on why “Why the generic name of the Nigerian Film Industry should be CineNaija” The “wood” suffix from the above is something I found an issue with in my recent article “Time to get out of the Woods.”
Like this:
Like Loading...