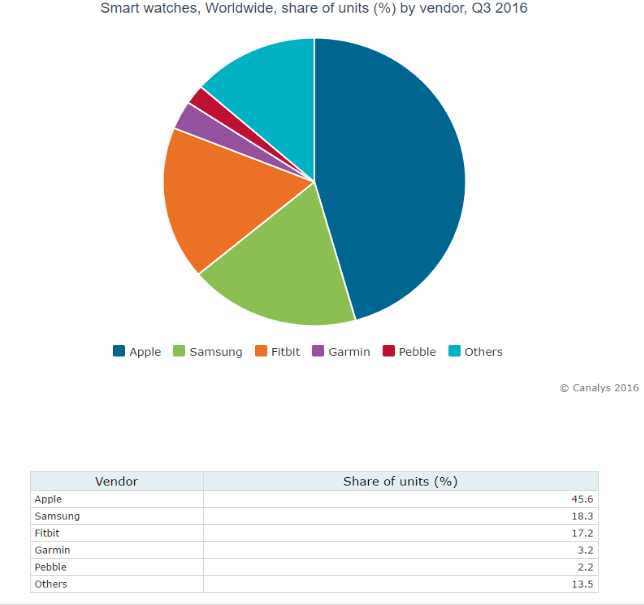
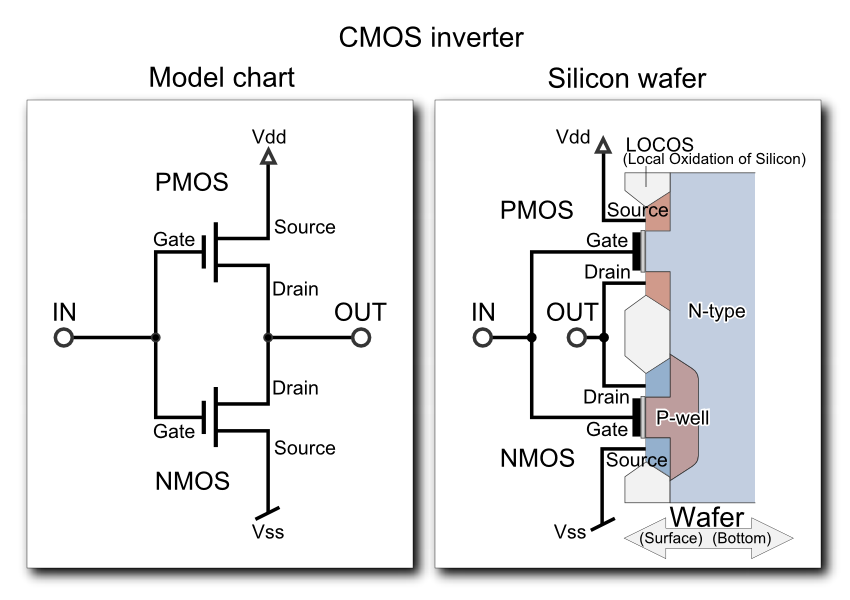
A solid idea is the essential foundation of a great infographic. While this may sound obvious, it is the most common mistake made by companies developing infographics today, leading to a slew of poorly thought-out visual disasters. I aim to spotlight a few of these pitfalls, to help you first recognize what you are trying to do, then identify the types of ideas that will help you achieve it.
Your primary consideration in choosing a topic should be your intended results. If you have a specific data set to visualize, or a concrete concept that needs to be explained visually, this will shape the direction immediately. However, if you are looking to utilize an infographic for marketing purposes and want to get as much mileage out of the piece as possible, you must choose your topic wisely. Do you want to provide an understanding of your product or service? Materials to support sales efforts? Brand exposure? Traffic and backlinks? Thought-leadership?
Want all of the above? Too bad. They all sound oh-so nice, but you can’t have them all at the same time. In fact, you can have very few of them if you want your graphic to be effective. Some of these can coexist with the right idea. Others are polar opposites, and will negate each other’s positive effects when combined. The way we think about graphics for the purpose of marketing is simple. There are two general directions you can take.
Brand Infographics
The first is the brand-centric infographic, which is based on a specific company or product. It explains the features of a product, unique processes, or company milestones or accomplishments. This is useful in presentations, sales materials, marketing collateral, or press releases. The target audiences are typically customers or potential customers, employees, or those in your specific industry who are aware of your company.
This graphic is incredibly useful for presenting a specific message to a very targeted audience. This also comes at a cost. By discussing something specific about your company, mass appeal is lost. This type of graphic is not going to get picked up by major news sites or go viral across the Web. As much as we would all like to think otherwise, when someone is looking for news online, they don’t want to read about your product. That is what advertising was for.
That is not to say that these graphics don’t provide a very real value. A visual depiction can often take information that is difficult to communicate verbally or in text and make it easily understood. This type of messaging is not only efficient, but also engages the target audience more than a traditional sales presentation, press release, or white paper.
I should also mention that there are exceptions to this. When a company has a passionate mainstream following, or has discovered something remarkable in their proprietary data, the stars can sometimes align to have this kind of content spread. Notable examples would be our recent piece for StumbleUpon, Mint’s data pieces, or this nostalgic timeline of Playstation’s history. Just know that the line here is very subtle, and instances of mainstream success are rare.
Editorial Infographics
The second type is the editorial infographic. This graphic is designed to have mass appeal, positioning the creator as an interesting source of information within an industry or on a specific topic. These infographics have the potential to be shared frequently online, bringing traffic, links, and brand exposure with it. These graphics should not include any references to your company in the content, but can include a company logo at the bottom to let people know the source of the information as it is shared online.
These infographics should cover interesting topics loosely related to your general industry. For example, a financial services company could display a breakdown of how the Federal Reserve Bank works, or a location-based service could cover a brief history of cartography. The broader and more interesting the topic, the better the graphic will perform. In order to be effective, brands must think of themselves as publishers. It may be difficult to resist the urge to promote the brand directly, but it is essential to an editorial infographic’s success.
How to Ruin Your Infographic
One of these options is not inherently better than the other. They serve very different purposes. It is essential that your marketing priorities are established before you choose your topic. The simplest way to ensure that you don’t achieve any of your objectives is to try to bridge the gap between the two. That is, choosing a somewhat broad editorial topic, then slipping in brand-mentions to try to derive as much branding value as possible. The audience is not stupid, and they know when they are being marketed to. This will create skepticism toward your content, which will quickly ruin any good vibes you had going with the audience.
For someone who eats, sleeps, and breathes the work of their company, it can be difficult to understand that even if the company is innovative, ambitious, and about to change the world, people don’t always want to hear about it. Rest assured that with a steady flow of engaging content, they will soon discover it on their own, as they become aware of the source of these informational graphics.
Let me know your thoughts on the matter @rtcrooks, @columnfive [Ross Crooks]. This piece was a guest post for Tekedia.
Like this:
Like Loading...