In continuation of our Understanding Digital Integrated Marketing Communication series, this piece examines how foreign and local brands use Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn for advertising and promotion. An analysis of over 100 brands reveals a sharp contrast in social media influence between foreign and local players.
Using follower count as the basis for determining engagement patterns, we found that foreign brands boast an average of 1,260,639 followers, dwarfing the local average of 165,810, a staggering difference of 1,094,829. This average is derived from a cumulative total of over 150 million followers across all the brands. This chasm in digital reach, as indicated in Exhibit 1, suggests a significant advantage for international brands in capturing online attention.
While a substantial follower count may suggest greater potential reach for advertising campaigns, the relationship between followers and engagement is far more complex. Our analysis, visualised in Exhibit 3, aligns with existing research indicating that likes are the most significant form of interaction followers have with brands during digital advertising or promotional periods.
Several factors could be contributing to the observed follower disparity. Ad Spend efficiency is a likely culprit. Foreign brands, with potentially larger marketing budgets, can invest more heavily in social media advertising, directly boosting their visibility and accelerating follower acquisition and by extension, more engagement with ads. The dominance of foreign brands on platforms like LinkedIn and Twitter also suggests a better alignment with the professional and global nature of these platforms, rather than solely superior content strategies.
Our analysis further indicates that audience demographics play a crucial role. Younger, urban populations might naturally gravitate towards the personas and messaging styles often adopted by foreign brands, leading to skewed engagement levels. Examining Exhibit 2, which details the frequency of deploying various social media content types, offers further insights into the engagement strategies employed by both groups.
The undeniable power imbalance in social media influence, as clearly illustrated, presents both a significant challenge and a compelling opportunity for local brands. The challenge lies in competing for attention in a digital ecosystem where international players often possess a considerable head start regarding reach and resources. However, this gap also allows local brands to strategically rethink their digital branding approaches and investment priorities to carve out their own competitive space.
Our analysis indicates a critical need for capacity building in digital marketing within the local business landscape. To effectively navigate this evolving digital terrain, local brands must move beyond simply replicating traditional marketing tactics online. They need to cultivate a deeper understanding of platform-specific nuances and audience engagement drivers.
Exhibit 1: Average follower count by brand location
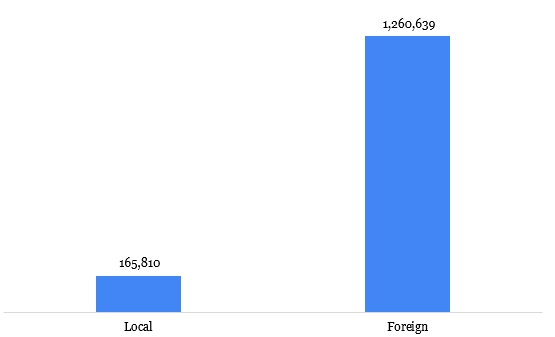
Exhibit 2: Frequency of deploying social media types by brand location
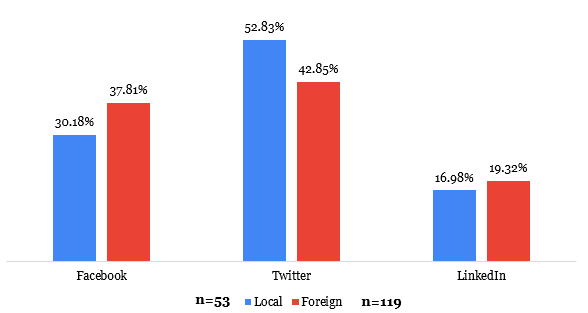
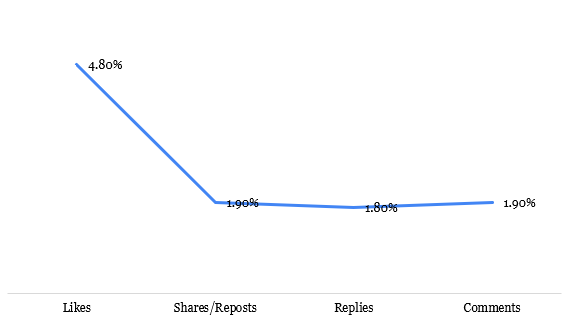
Exhibit 3: Percentage of follower count in engagement pattern
To bridge the digital divide and foster stronger online connections, local brands may need to recognise that each social media platform caters to a unique audience and content format is paramount. Tailoring content and advertising approaches specifically for Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn, rather than employing a one-size-fits-all strategy, can significantly enhance engagement and follower growth.
One of the inherent advantages local brands possess is their deep understanding of the local culture, contexts and consumer needs. Crafting compelling narratives that resonate with the local audience, incorporating cultural references, and addressing specific local concerns can foster a stronger sense of connection and loyalty.
Collaborating with local influencers who have established trust and credibility within the target demographic can be a powerful way to expand reach and drive engagement. These partnerships can lend authenticity and relatability that might be harder for foreign brands to replicate.
Building a recognisable and consistent brand identity across all digital touchpoints is crucial for establishing trust and fostering a loyal following. Authenticity in messaging and engagement can help local brands stand out in a crowded digital space.
Infoprations’ Understanding Digital Integrated Marketing Communications Team includes Abdulazeez Sikiru Zikirullah, Moshood Sodiq Opeyemi, and Bello Opeyemi Zakariyha






