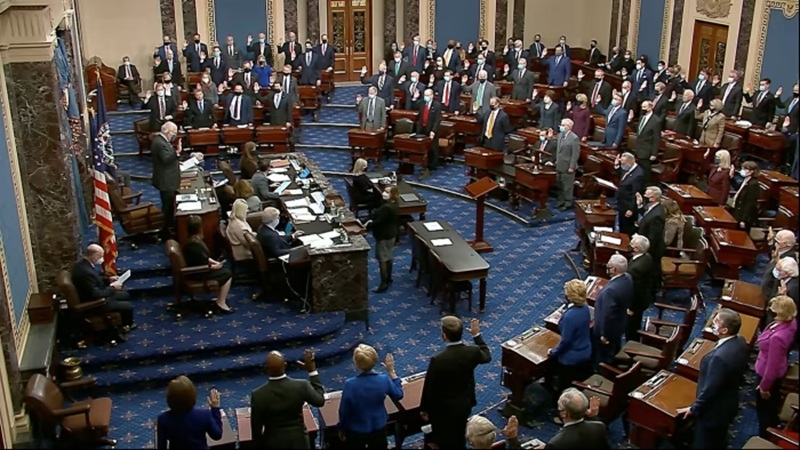
The US House of Representatives issued a formal call for the Senate to expedite and pass comprehensive crypto market structure legislation before the month concludes.
This push underscores mounting pressure to deliver regulatory clarity for digital assets amid a rapidly evolving industry and bipartisan momentum in Congress.
The move aligns with ongoing negotiations and builds on earlier House actions, signaling that the window for action in the current session is narrowing. The core bill in question is the Digital Asset Market Clarity Act of 2025 (CLARITY Act), a 236-page framework that passed the House in July 2025 with strong bipartisan support (294-134 vote).
It aims to delineate regulatory jurisdiction between the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC): For “digital commodities”— Bitcoin-like assets in spot markets, emphasizing anti-manipulation rules and exchange standards to curb scams like “rug pulls.”
SEC role, retained for securities-like tokens, with provisions for dual registration for platforms handling both. Key protections includes investor safeguards, custody requirements, and exemptions for certain decentralized finance (DeFi) elements, while addressing illicit finance and state-level preemption.
This follows the successful passage of the Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins (GENIUS) Act in July 2025, which established rules for stablecoin issuers like reserve backing and anti-money laundering compliance and has already been signed into law.
The CLARITY Act represents the next pillar in a “trilogy” of crypto reforms, with the third focusing on anti-CBDC measures.The Senate has been working on its version since November 2025, with the Banking and Agriculture Committees releasing discussion drafts.
These emphasize CFTC primacy for non-security tokens, DeFi guidelines though still underdeveloped, and anti-manipulation standards for exchanges. Senate Banking Chair Tim Scott (R-SC) has targeted a December markup, with hopes for early 2026 passage to President Trump’s desk, who has positioned the US as the “crypto capital of the world.”
Congress adjourns for the holidays soon after December 31, risking a stall into the next session where priorities could shift. Crypto executives, including Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong, have lobbied intensely, warning that delays hinder US innovation.
The sector has poured hundreds of millions into campaigns, viewing clarity as essential for growth. Talks stalled in October over DeFi rules and Democratic concerns about President Trump’s family crypto ties (e.g., potential conflicts). Recent CEO meetings with senators like Cynthia Lummis (R-WY) and Mark Warner (D-VA) aim to restart negotiations.
Without passage, ongoing SEC-CFTC turf wars persist, stifling institutional adoption. Proponents argue it could “unlock US crypto growth” by reducing regulatory arbitrage. Some Senate Democrats, led by Elizabeth Warren, criticize the bills for weak consumer protections and Trump’s conflicts, pushing for stricter DeFi oversight.
Unlike the House’s version, the Senate may expand exemptions and refine jurisdictional lines, requiring House reconciliation. High for markup, but full passage by month-end is uncertain—experts peg it at 60-70% if bipartisan tweaks land.
White House Crypto Czar David Sacks has echoed the September call now exbtended, urging swift action. If passed, it would mark a historic shift, potentially catalyzing a surge in crypto adoption and valuations. Watch for Senate updates in the coming weeks—failure to act could delay reforms until mid-2026.