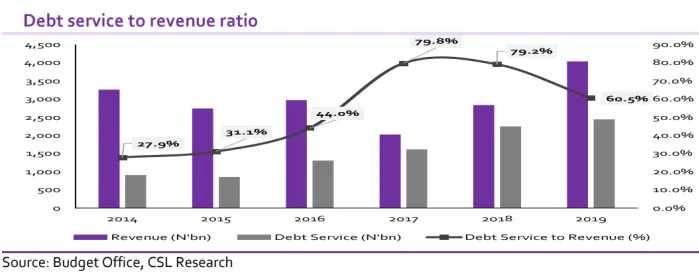
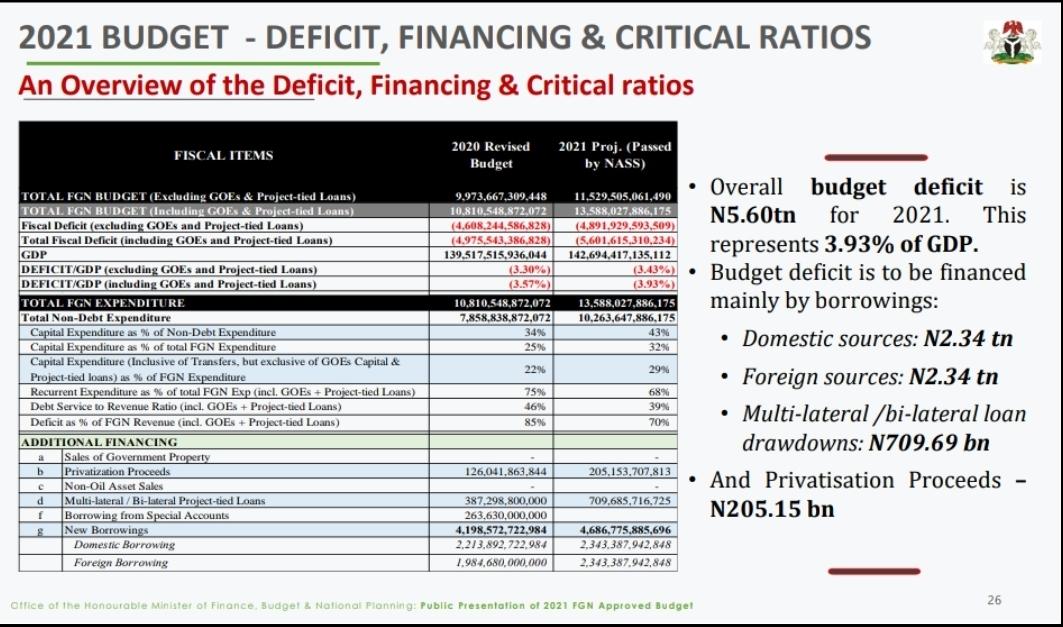
Saheed Aderinto is a US based Nigerian academic. He is a Professor of History at the Western Carolina University. This piece is his speech at the inaugural Pius Adesanmi Webinar Series held on Friday 15 January, 2021.
I am honored to be invited to speak at this inaugural Pius Adesanmi Webinar Series. During his lifetime, Adesanmi committed significant energy to mentoring up-and-coming scholars through academic networks in North America and Africa. He wrote thought-provoking articles and spoke truth to power. He was intellectually brave, not a coward. Any project honoring his legacy must follow his footstep.
My speech will insert suggestions on what should be the role of mentors and academic networks and communities into the structural problems that militate against quality knowledge production in Africa. The common manual for building academic networks prescribes attending seminars and conferences, contacting scholars, and publishing in areas of specialization. But, research has shown that many factors, including but not limited to gender, race, location, funding, and even ethnicity and religion make it difficult for up-and-coming scholars to build their own network all by themselves. Effective networking is also about personality, which varies from individual to individual. We always expect scholars to network, but we rarely reflect on the difficulty they encounter in doing so. Networking, like everything else, is not a level playing field.
This is where senior scholars, working through associations and networks, must come in. An ideal network must provide a conducive environment for early career scholars to learn from senior scholars without feeling intimidated or entrapped. A space where senior scholars could give back and invest intellectually in budding scholars, without feeling entitled to anything from them. A serious academic community building must correct the imbalance in the distribution of opportunities for professional development. It must work to close achievement gaps between scholars. African studies needs a community of deep thinkers that is inclusive and that allows respectful intergenerational relationship around issues of mutual importance. Senior scholars must not invest in themselves or activities that directly enhance their status alone, but in academic networks that improve the professional development of the larger community. Institutions are stronger when their ideals go beyond the personal, the individual, self-legacy building. Rather, we need reading groups and clusters that are connected to the main grid of global knowledge production. We need regular departmental seminars, where scholars present their work-in-progress. A non-combative departmental seminar where ideas, not references and citation styles and punctuation marks, are debated.
Building an academic community around senior scholars, journal editors, book series editors, and research grant awarding institutions whose work represents the highest level of originality and integrity is not enough to create a space for junior scholars to grow. We need to address such important matters as conference registration and membership fees. Many junior academics in Africa are unable to present at conferences organized on their campuses because they cannot afford registration fees. Deliberations about how, what, and where conference attendees would eat should be as important as the quality of the conference programs. We all know that networking does not happen during panel discussions but at hotel lobbies, and during meals and informal gatherings. By providing food onsite, panel conversations would continue and assume new life during mealtime, thus elongating the physical contact needed to build professional networks. Even the most introverted academics would find their voices in such spaces. With the current exchange rate of the Naira, an early career Nigerian academic attending a self-sponsored conference in New York would think twice before buying a burger, if the organizer fails to provide food. The time spent looking for affordable food and commuting from affordable hotels (because the conference hotel is too expensive) is a wasted networking time.
The problem of intellectual community building in Africa is not the lack of intellectuals, but the paucity of intellectual leadership capable of driving sustainable mentorship projects through new and existing networks. Academic associations must be more than conference organizers; they must have a clear and consistent agenda for professional development of junior academics. Conferences must include seminars on teaching pedagogy, journal and book writing, network building, and work-life balance. A ninety-minute preconference session on how to avoid plagiarism is more valuable to an amateur scholar than listening to four poorly researched and thoughtless papers at a conference. Professional development workshops would have limited impact if there is no avenue for follow-ups, which could be done through emails and social media, where members share career news, new publications, and opportunities. Similarly, academic associations must acknowledge inequalities, among other structural problems within their field, and work to address them. A strong academic network is not the one without the problems of unfairness caused by location, race, gender, and access to resources; rather, it is the one that recognizes the need to mend these gaps because of a shared goal of promoting best practices in knowledge production and dissemination. Intellectual activism should be an integral part of intellectual community building.
I agree with the Council for the Development of Social Science Research Africa (CODESRIA) that academic journal publishing by Africa-based scholars have increased tremendously in the past two decades. Thanks to the internet, virtual library, and information technology, African graduate students and junior academics today can conduct research faster than their 20th century predecessors. Paradoxically, this new development did not translate to quality research output because of plagiarism, bad writing, and poor research skills. For me, African studies doesn’t need more books and journal articles, but books and journal articles with more originality, more creativity, and more rigor. We need to open new archives, properly secure existing ones, and work with archivists to establish a mutually beneficial relationship.
The problem of knowledge production in Africa is not the lack of original data, but inadequate training to see data in everything and everywhere. Edited volumes and syntheses have their own merits, if properly executed; but they are not the future of African knowledge production. The future is in rigorously researched monographs and journal articles, new archeological discoveries, clever literary works, jaw-dropping art and art exhibitions, and path-breaking documentaries and films, among other modes of knowledge production and dissemination. A lot of the scholarship coming out of Africa are substandard, not because of a dearth of brilliant minds, but a skewed conception of academic progress and global intellectual visibility, promoted by some senior scholars in Africa and the diaspora—in addition to other structural problems like funding. Not all international publications would give Africa-based scholars global intellectual visibility. Creativity, originality, rigor of writing and research, integrity and thoroughness of peer review, as well as outlet, all matter.
Today, most of the universities established before the 21st century have alumni scholars, working in universities across the world. Academic alumni lectures, seminars, and professional development series should be built into the core curriculum of each department. They shouldn’t be a one-time event that is more about the invited guest than about the institution and their students. Departments can leverage on the proliferation of virtual lectures due to the COVID-19 pandemic to invite former students to classes. Mobilizing alumni to improve curriculum development is not rocket science, if the will to do it exists. An average alumnus would like to give back, regardless of their experience during their school days, if they are given the opportunity. If people in the business and corporate world can create powerful alumni networks for professional development, there is no reason each department cannot build sustainable academic relationship with their alumni across the world. Human and inter-personal differences, which inhibit alumni-centered academic networks have an expiry date, but institutions can exist forever. Therefore, institution-building must take precedence over individual differences.
The problem of mentorship is not the lack of mentors, but the fewness of mentors who focus on improving the writing, thinking, and research skills of their mentees—beyond being doctoral supervisors who want graduate students just for academic wardship. Academic mentorship is not synonymous with academic wardship. Doctoral supervisors don’t automatically become mentors if their present and past students are deprived of intellectual independence, rigorous training, and academic integrity. Real mentors would teach their mentees to depend on them to the extent that they can do without them. The enemy of African knowledge production is greedy mentorship legitimized as “normal” and “appropriate” because established scholars do it.
To worsen predacious mentorship, many universities insist that graduate students must publish chapters of their doctoral thesis with their supervisors as a condition for graduation. This commodification of mentorship has deprived many brilliant young minds the opportunity to own their own ideas and secure intellectual visibility. The fact that something is approved by university authorities does not mean it is right. Instead of making regulations that favor cannibalizing graduate students’ doctoral thesis, even before they are defended, universities should promote advanced digital academic communities that allow graduate students to share their work-in-progress. Academic WhatsApp groups and social media platforms, in addition to sharing academic resources, should focus on building dialectic and critical thinking than debating pedestrian, common-place matters that don’t merit the time of any serious intellectual.
True mentoring is a selfless job, for which a genuine mentor should expect nothing in return other than—Thank You! If selective kindness is not kindness, selective mentorship cannot be mentorship. Mentors who are nice to some people and mean to those who refuse to venerate them, or be exploited by them, are not mentors, but tormentors. A mentor who makes co-authoring the only condition for mentorship is not a mentor, but a greedy academic. A true mentor would help their mentees to claim a space in the galaxy of ideas—rightfully, ethically, respectfully, and honorably. Because the mentee of today is the mentor of tomorrow, training on how to be a good mentor should be part of professional development. Indeed, mentoring has some practical components that can be taught to all scholars, regardless of academic rank. Mentoring is also art. The best mentors combine the practical with the artistic.
Africa-based junior scholars don’t need anyone to help them publish—in the worst-case scenario, they can always publish in vanity journals or in edited volumes that belong nowhere but the trash can. What they need is serious discussion about their role as knowledge producers, a guide on how to write well, conduct rigorous research, mine compact data, read sources beyond the obvious, hone their contribution within extant literature, and engage with ideas that straddle multiple discursive frames. There is no component of professional development that is not teachable. For me, if the process is truly rigorous, the outcome would not only be good, but can be replicated, many times, independently. So, I encourage my mentees to focus on the process, not on the outcome.
Improved facilities, funding for research, and salary increase alone won’t solve the crisis confronting university education in Africa. Mentee-to-mentor ratio must reduce. A new cultural awakening about mentorship is required. The university system itself needs a rebirth to create a space where junior scholars are protected from hazing and bullying from their senior counterparts. A space where everyone is respected regardless of whether they have a PhD or are professors or not. The system needs to create spaces where hazing is not dressed in gerontocratic and professorial garments. A democratic approach to intellectual community building that allows everyone, regardless of gender, age, location, to voice their perspective without any fear of retribution is fundamental. The villain should never be made the victim. To truncate the channels that reproduce intellectual servitude and hazing, early career scholars need role models who derive their legitimacy from upholding academic integrity and from being kind-hearted top-notch researchers, not from academic titles and ranks alone.
If it is hard to build serious academic networks and secure non-predatory and committed mentors, it is harder to sustain them. For academic mentorship and network building to stand the test of time at the institutional level, they must be motivated by a desire to institutionalize something new and creative, not an agenda to make a short-lived administrative statement. Some mentorship and academic network projects died, even before they were born; they became stillborn because they were built around specific university administration, rather than implanted into the academic culture of the university. Hence, I would recommend that mentorship projects extend beyond an individual’s or an administration’s idea to an institutionalized one, with a clear path for growth, sustenance, and prosperity.
I don’t claim that some individuals, associations, and institutions have not been thinking and acting along the suggestions outlined above. The conversation about what exactly should be the role of mentors in professional development in Africa and the diaspora should be an unending one. Whenever we have this conversation, we should refuse to cave in to intimidation from people and institutions who perpetrate violent exploitation of mentees under the ruse of mentoring. The conversation is bigger than an individual or any particular institution of higher learning. The matter, like the one on sexual harassment in higher education, shouldn’t be trivialized by pseudo-intellectual, uncritical, sheep-following narratives. We shouldn’t succumb to the language of intellectual servitude deployed by individuals who have substituted critical thinking for academic patronage—the greatest threat to originality, creativity, and integrity. A scholar doesn’t mature by being complacent, but by being intellectually independent, outspoken, and selflessly investing in others. It is inappropriate to view genuine criticism as an act of “disrespect” or “ingratitude,” but as the oil that lubricates the wheel of intellectual progress.
Like this:
Like Loading...